Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Mercury (12)
- (-) Net Zero (12)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (116)
- Advanced Reactors (34)
- Artificial Intelligence (87)
- Big Data (50)
- Bioenergy (88)
- Biology (96)
- Biomedical (58)
- Biotechnology (21)
- Buildings (55)
- Chemical Sciences (60)
- Clean Water (29)
- Climate Change (94)
- Composites (25)
- Computer Science (184)
- Coronavirus (46)
- Critical Materials (25)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Decarbonization (75)
- Education (4)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (107)
- Environment (192)
- Exascale Computing (36)
- Fossil Energy (5)
- Frontier (41)
- Fusion (53)
- Grid (61)
- High-Performance Computing (83)
- Hydropower (11)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (49)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (46)
- Materials (141)
- Materials Science (136)
- Mathematics (6)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (51)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Nanotechnology (60)
- National Security (59)
- Neutron Science (130)
- Nuclear Energy (105)
- Partnerships (40)
- Physics (59)
- Polymers (31)
- Quantum Computing (31)
- Quantum Science (66)
- Renewable Energy (2)
- Security (24)
- Simulation (45)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (25)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (57)
- Sustainable Energy (121)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (7)
- Transportation (94)
Media Contacts

As renewable sources of energy such as wind and sun power are being increasingly added to the country’s electrical grid, old-fashioned nuclear energy is also being primed for a resurgence.

Matthew Craig grew up eagerly exploring the forest patches and knee-high waterfalls just beyond his backyard in central Illinois’ corn belt. Today, that natural curiosity and the expertise he’s cultivated in biogeochemistry and ecology are focused on how carbon cycles in and out of soils, a process that can have tremendous impact on the Earth’s climate.

What’s getting Jim Szybist fired up these days? It’s the opportunity to apply his years of alternative fuel combustion and thermodynamics research to the challenge of cleaning up the hard-to-decarbonize, heavy-duty mobility sector — from airplanes to locomotives to ships and massive farm combines.

Spanning no less than three disciplines, Marie Kurz’s title — hydrogeochemist — already gives you a sense of the collaborative, interdisciplinary nature of her research at ORNL.
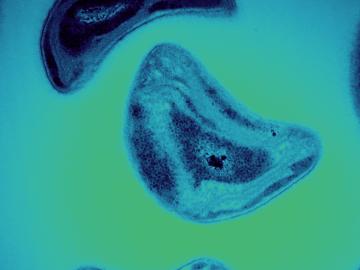
A team led by ORNL and the University of Michigan have discovered that certain bacteria can steal an essential compound from other microbes to break down methane and toxic methylmercury in the environment.
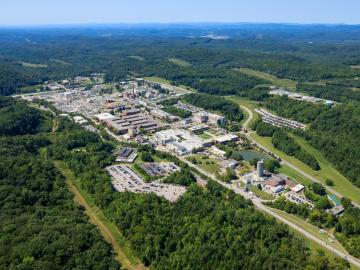
Anyone familiar with ORNL knows it’s a hub for world-class science. The nearly 33,000-acre space surrounding the lab is less known, but also unique.

Moving to landlocked Tennessee isn’t an obvious choice for most scientists with new doctorate degrees in coastal oceanography.
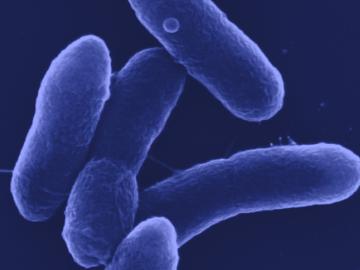
A research team led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory bioengineered a microbe to efficiently turn waste into itaconic acid, an industrial chemical used in plastics and paints.

New capabilities and equipment recently installed at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are bringing a creek right into the lab to advance understanding of mercury pollution and accelerate solutions.
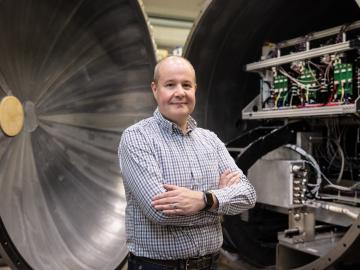
Sometimes solutions to the biggest problems can be found in the smallest details. The work of biochemist Alex Johs at Oak Ridge National Laboratory bears this out, as he focuses on understanding protein structures and molecular interactions to resolve complex global problems like the spread of mercury pollution in waterways and the food supply.