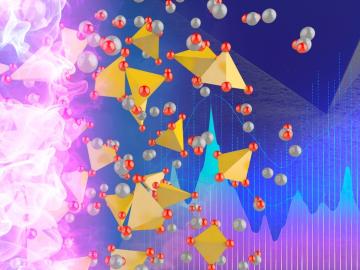
As current courses through a battery, its materials erode over time. Mechanical influences such as stress and strain affect this trajectory, although their impacts on battery efficacy and longevity are not fully understood.

As current courses through a battery, its materials erode over time. Mechanical influences such as stress and strain affect this trajectory, although their impacts on battery efficacy and longevity are not fully understood.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists designed a recyclable polymer for carbon-fiber composites to enable circular manufacturing of parts that boost energy efficiency in automotive, wind power and aerospace applications.
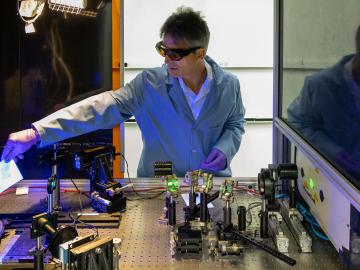
A multidisciplinary team of scientists at ORNL has applied a laser-interference structuring, or LIS, technique that makes significant strides toward eliminating the need for hazardous chemicals in corrosion protection for vehicles.
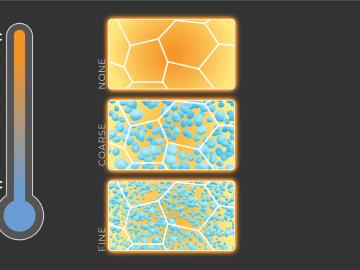
Scientists at ORNL and the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have found a way to simultaneously increase the strength and ductility of an alloy by introducing tiny precipitates into its matrix and tuning their size and spacing.

Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory demonstrated that an additively manufactured polymer layer, when applied to carbon fiber reinforced plastic, or CFRP, can serve as an effective protector against aircraft lightning strikes.

Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory will present eight innovative technologies currently available for commercialization during a public event at ORNL on October 17.

Six new nuclear reactor technologies are set to deploy for commercial use between 2030 and 2040. Called Generation IV nuclear reactors, they will operate with improved performance at dramatically higher temperatures than today’s reactors.

In the shifting landscape of global manufacturing, American ingenuity is once again giving U.S companies an edge with radical productivity improvements as a result of advanced materials and robotic systems developed at the Department of Energy’s Manufac
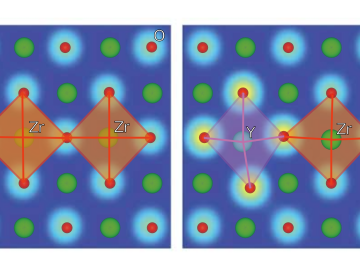
Ionic conduction involves the movement of ions from one location to another inside a material. The ions travel through point defects, which are irregularities in the otherwise consistent arrangement of atoms known as the crystal lattice.

A successful test of 3D-printed thermoplastic molds demonstrates the potential of additive manufacturing in the tooling industry.

