
In fiscal year 2023 — Oct. 1–Sept. 30, 2023 — Oak Ridge National Laboratory was awarded more than $8 million in technology maturation funding through the Department of Energy’s Technology Commercialization Fund, or TCF.

In fiscal year 2023 — Oct. 1–Sept. 30, 2023 — Oak Ridge National Laboratory was awarded more than $8 million in technology maturation funding through the Department of Energy’s Technology Commercialization Fund, or TCF.
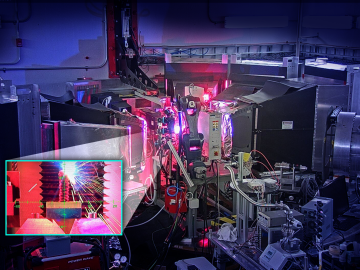
Using neutrons to see the additive manufacturing process at the atomic level, scientists have shown that they can measure strain in a material as it evolves and track how atoms move in response to stress.
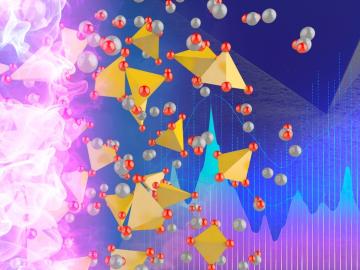
As current courses through a battery, its materials erode over time. Mechanical influences such as stress and strain affect this trajectory, although their impacts on battery efficacy and longevity are not fully understood.
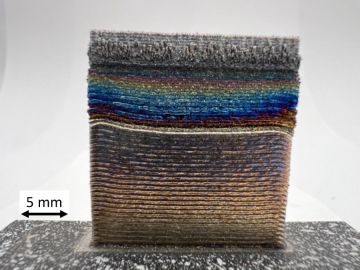
Research into a new, unique technology to fabricate composite metal parts for a wide range of applications operating in extreme environments across the aviation, space and energy industries is showing promise for additive manufacturing.

Scientists at ORNL have invented a coating that could dramatically reduce friction in common load-bearing systems with moving parts, from vehicle drive trains to wind

Stan David, retired scientist and Corporate Fellow Emeritus at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was awarded the Joining and Welding Science Award from the Joining and Welding Research Institute at Osaka University, Japan.

Andrew Ullman, Distinguished Staff Fellow at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, is using chemistry to devise a better battery

Nine engineers from ORNL visited 10 elementary and middle school classrooms in three school districts during National Engineers Week, Feb.
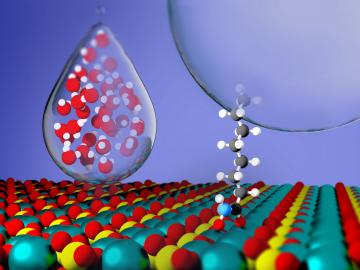
Critical Materials Institute researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Arizona State University studied the mineral monazite, an important source of rare-earth elements, to enhance methods of recovering critical materials for energy, defense
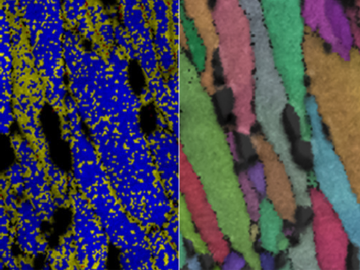
ORNL researchers have identified a mechanism in a 3D-printed alloy – termed “load shuffling” — that could enable the design of better-performing lightweight materials for vehicles.

