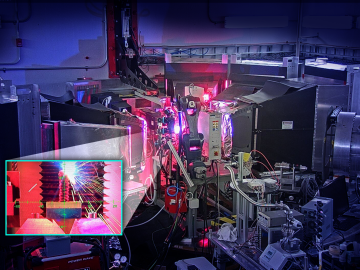
Using neutrons to see the additive manufacturing process at the atomic level, scientists have shown that they can measure strain in a material as it evolves and track how atoms move in response to stress.

Using neutrons to see the additive manufacturing process at the atomic level, scientists have shown that they can measure strain in a material as it evolves and track how atoms move in response to stress.

Since its inception in 2010, the program bolsters national scientific discovery by supporting early career researchers in fields pertaining to the Office of Science.
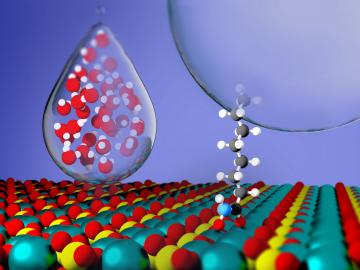
Critical Materials Institute researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Arizona State University studied the mineral monazite, an important source of rare-earth elements, to enhance methods of recovering critical materials for energy, defense
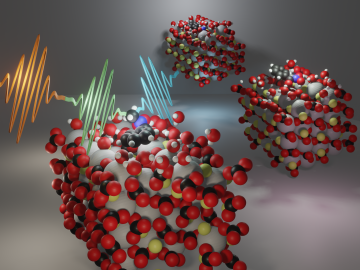
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are using state-of-the-art methods to shed light on chemical separations needed to recover rare-earth elements and secure critical materials for clean energy technologies.
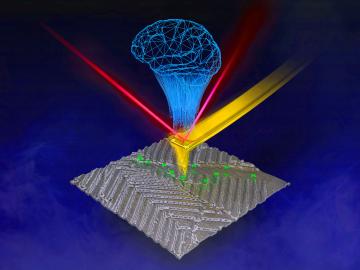
Researchers at ORNL are teaching microscopes to drive discoveries with an intuitive algorithm, developed at the lab’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, that could guide breakthroughs in new materials for energy technologies, sensing and computing
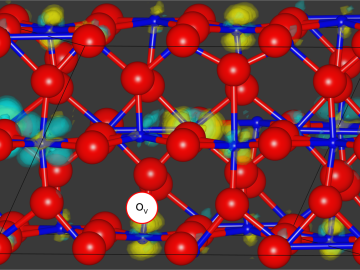
Neuromorphic devices — which emulate the decision-making processes of the human brain — show great promise for solving pressing scientific problems, but building physical systems to realize this potential presents researchers with a significant
A multidisciplinary team of scientists at ORNL has applied a laser-interference structuring, or LIS, technique that makes significant strides toward eliminating the need for hazardous chemicals in corrosion protection for vehicles.

Six ORNL scientists have been elected as fellows to the American Association for the Advancement of Science, or AAAS.
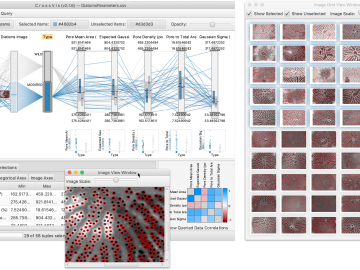
From materials science and earth system modeling to quantum information science and cybersecurity, experts in many fields run simulations and conduct experiments to collect the abundance of data necessary for scientific progress.

Joe Paddison, a Eugene P. Wigner Fellow at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, believes there’s more information to be found in neutron scattering data than scientists like himself might expect.

