
Quantum computers process information using quantum bits, or qubits, based on fragile, short-lived quantum mechanical states.

Quantum computers process information using quantum bits, or qubits, based on fragile, short-lived quantum mechanical states.

Zheng Gai, a senior staff scientist at ORNL’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, has been selected as editor-in-chief of the Spin Crossover and Spintronics section of Magnetochemistry.
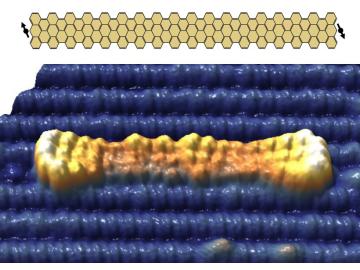
An international multi-institution team of scientists has synthesized graphene nanoribbons – ultrathin strips of carbon atoms – on a titanium dioxide surface using an atomically precise method that removes a barrier for custom-designed carbon
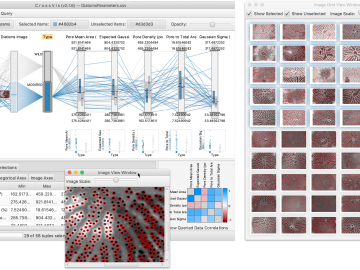
From materials science and earth system modeling to quantum information science and cybersecurity, experts in many fields run simulations and conduct experiments to collect the abundance of data necessary for scientific progress.

Joe Paddison, a Eugene P. Wigner Fellow at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, believes there’s more information to be found in neutron scattering data than scientists like himself might expect.

Students often participate in internships and receive formal training in their chosen career fields during college, but some pursue professional development opportunities even earlier.

Raphaël Hermann of the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory conducts experiments to better understand materials for energy and information applications.

The lighter wand for your gas BBQ, a submarine’s sonar device and the ultrasound machine at your doctor’s office all rely on piezoelectric materials, which turn mechanical stress into electrical energy, and vice versa.
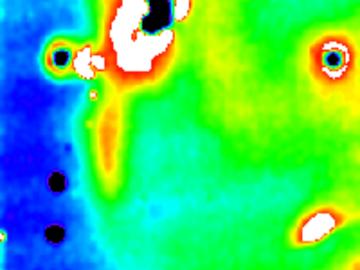
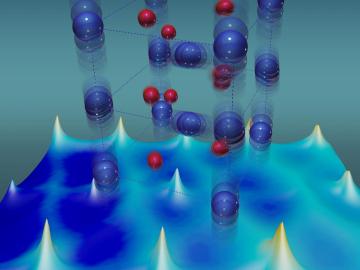
For more than 50 years, scientists have debated what turns particular oxide insulators, in which electrons barely move, into metals, in which electrons flow freely.

