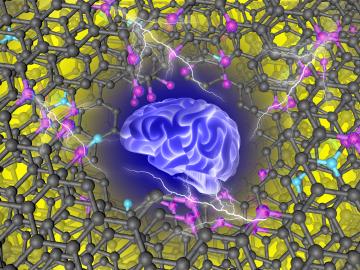
Guided by machine learning, chemists at ORNL designed a record-setting carbonaceous supercapacitor material that stores four times more energy than the best commercial material.

Guided by machine learning, chemists at ORNL designed a record-setting carbonaceous supercapacitor material that stores four times more energy than the best commercial material.
When the second collaborative ORNL-Vanderbilt University workshop took place on Sept. 18-19 at ORNL, about 70 researchers and students assembled to share thoughts concerning a broad spectrum of topics.

Quantum computers process information using quantum bits, or qubits, based on fragile, short-lived quantum mechanical states.

Since its inception in 2010, the program bolsters national scientific discovery by supporting early career researchers in fields pertaining to the Office of Science.

Ho Nyung Lee, a condensed matter physicist at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been elected a Fellow of the Materials Research Society.
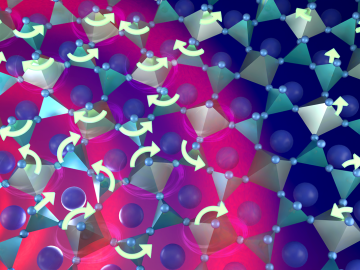
Warming a crystal of the mineral fresnoite, ORNL scientists discovered that excitations called phasons carried heat three times farther and faster than phonons, the excitations that usually carry heat through a material.

ORNL has been selected to lead an Energy Frontier Research Center, or EFRC, focused on polymer electrolytes for next-generation energy storage devices such as fuel cells and solid-state electric vehicle batteries.

Scientists at ORNL used neutron scattering to determine whether a specific material’s atomic structure could host a novel state of matter called a spiral spin liquid.
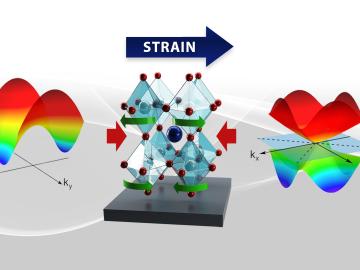
A team led by the ORNL has found a rare quantum material in which electrons move in coordinated ways, essentially “dancing.”
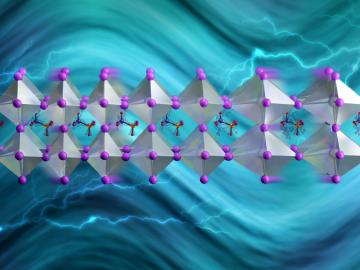
Led by ORNL and the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, a study of a solar-energy material with a bright future revealed a way to slow phonons, the waves that transport heat.

