
The interaction of elemental iron with the vast stores of carbon locked away in Arctic soils is key to how greenhouse gases are emitted during thawing and should be included in models used to predict Earth’s climate.

The interaction of elemental iron with the vast stores of carbon locked away in Arctic soils is key to how greenhouse gases are emitted during thawing and should be included in models used to predict Earth’s climate.

ORNL appointed Peter Thornton as director of its Climate Change Science Institute, or CCSI, effective November 1, 2022.

Matthew Craig grew up eagerly exploring the forest patches and knee-high waterfalls just beyond his backyard in central Illinois’ corn belt.

The Earth System Grid Federation, a multi-agency initiative that gathers and distributes data for top-tier projections of the Earth’s climate, is preparing a series of upgrades.

ORNL researchers are deploying their broad expertise in climate data and modeling to create science-based mitigation strategies for cities stressed by climate change as part of two U.S. Department of Energy Urban Integrated Field Laboratory projects.
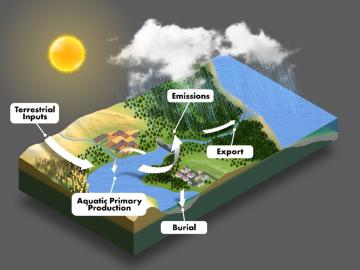
Global carbon emissions from inland waters such as lakes, rivers, streams and ponds are being undercounted by about 13% and will likely continue to rise given climate events and land use changes, ORNL scientists found.
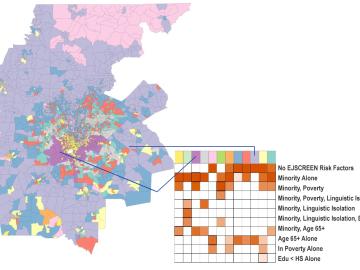
A new capability to identify urban neighborhoods, down to the block and building level, that are most vulnerable to climate change could help ensure that mitigation and resilience programs reach the people who need them the most.

Technology developed at ORNL to monitor plant productivity and health at wide scales has been licensed to Logan, Utah-based instrumentation firm Campbell Scientific Inc.

Tackling the climate crisis and achieving an equitable clean energy future are among the biggest challenges of our time.

Tackling the climate crisis and achieving an equitable clean energy future are among the biggest challenges of our time.

