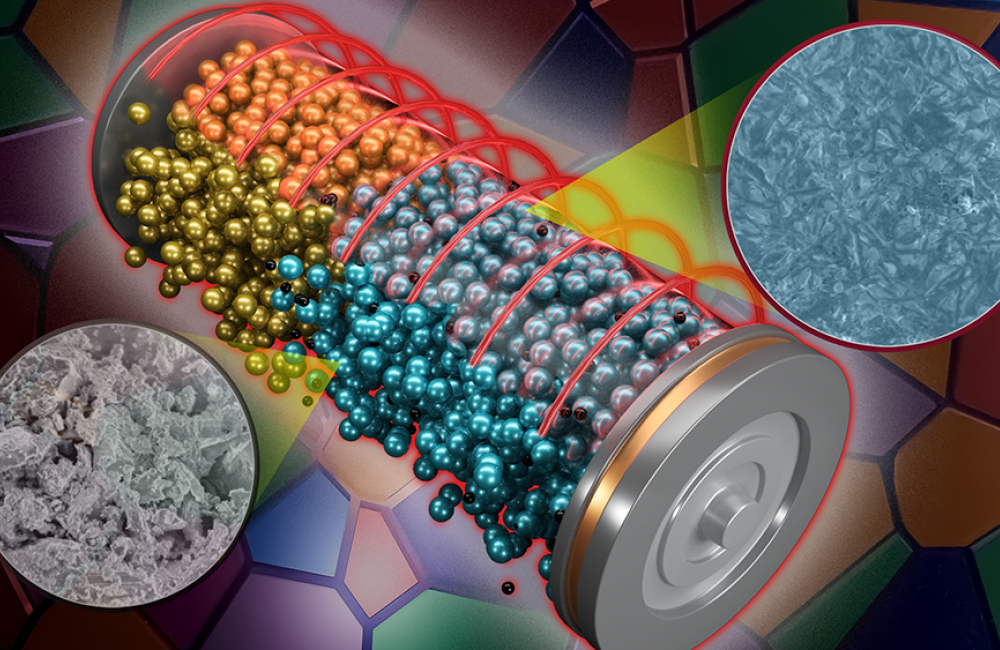
ORNL researchers have developed a new pressing method, shown as blue circle on right, that produces a more uniform solid electrolyte than the traditionally processed material with more voids, shown as gray circle on left. The material can be integrated into a battery system, center, for improved stability and rate performance. Credit: Andy Sproles/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists found that a small tweak created big performance improvements in a type of solid-state battery, a technology considered vital to broader electric vehicle adoption.
These batteries use a solid electrolyte instead of a potentially flammable liquid. When the battery charges or operates, ions move between electrodes through the electrolyte between them. A new method for pressing the solid electrolyte practically eliminates tiny air pockets that block ion flow, so the battery charges twice as fast.
ORNL lead researcher Marm Dixit said the approach involved heating the press after spreading the electrolyte on it, then letting the electrolyte cool under pressure. The resulting material was almost 1,000 times more conductive. “It’s the same material — you’re just changing how you make it, while improving the battery performance on a number of fronts,” Dixit said.
These results demonstrate a pathway for processing solid electrolytes at an industrial scale while providing unprecedented control over their internal structure for a more reliable battery.