
Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Isotopes (25)
- (-) Machine Learning (31)
- (-) Materials Science (64)
- (-) Mathematics (9)
- (-) Microscopy (12)
- (-) Nanotechnology (19)
- (-) Quantum Science (36)
- (-) Space Exploration (5)
- (-) Transportation (30)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (58)
- Advanced Reactors (19)
- Artificial Intelligence (53)
- Big Data (39)
- Bioenergy (30)
- Biology (27)
- Biomedical (35)
- Biotechnology (12)
- Buildings (30)
- Chemical Sciences (35)
- Clean Water (8)
- Composites (12)
- Computer Science (85)
- Coronavirus (25)
- Critical Materials (10)
- Cybersecurity (4)
- Education (2)
- Emergency (3)
- Energy Storage (36)
- Environment (67)
- Exascale Computing (28)
- Fossil Energy (4)
- Frontier (22)
- Fusion (26)
- Grid (23)
- High-Performance Computing (48)
- Hydropower (1)
- ITER (2)
- Materials (26)
- Mercury (1)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Molten Salt (3)
- National Security (36)
- Neutron Science (59)
- Nuclear Energy (47)
- Partnerships (29)
- Physics (22)
- Polymers (12)
- Quantum Computing (20)
- Security (11)
- Simulation (24)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (31)
Media Contacts

About 60 years ago, scientists discovered that a certain rare earth metal-hydrogen mixture, yttrium, could be the ideal moderator to go inside small, gas-cooled nuclear reactors.

Scientists at ORNL and the University of Nebraska have developed an easier way to generate electrons for nanoscale imaging and sensing, providing a useful new tool for material science, bioimaging and fundamental quantum research.

Kübra Yeter-Aydeniz, a postdoctoral researcher, was recently named the Turkish Women in Science group’s “Scientist of the Week.”

Radioactive isotopes power some of NASA’s best-known spacecraft. But predicting how radiation emitted from these isotopes might affect nearby materials is tricky

Researchers at ORNL used quantum optics to advance state-of-the-art microscopy and illuminate a path to detecting material properties with greater sensitivity than is possible with traditional tools.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have discovered a cost-effective way to significantly improve the mechanical performance of common polymer nanocomposite materials.
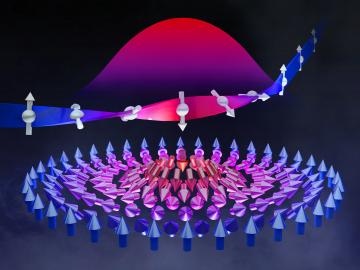
Scientists discovered a strategy for layering dissimilar crystals with atomic precision to control the size of resulting magnetic quasi-particles called skyrmions.

The Department of Energy has selected Oak Ridge National Laboratory to lead a collaboration charged with developing quantum technologies that will usher in a new era of innovation.

A team led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a novel, integrated approach to track energy-transporting ions within an ultra-thin material, which could unlock its energy storage potential leading toward faster charging, longer-lasting devices.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have developed artificial intelligence software for powder bed 3D printers that assesses the quality of parts in real time, without the need for expensive characterization equipment.


