
Filter News
Area of Research
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (7)
- (-) Biomedical (16)
- (-) Environment (20)
- (-) Fusion (11)
- (-) Isotopes (7)
- (-) Materials Science (30)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (25)
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Big Data (8)
- Bioenergy (15)
- Biology (5)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (1)
- Chemical Sciences (5)
- Clean Water (2)
- Composites (1)
- Computer Science (36)
- Coronavirus (22)
- Critical Materials (2)
- Cybersecurity (4)
- Energy Storage (15)
- Exascale Computing (4)
- Grid (4)
- High-Performance Computing (3)
- Machine Learning (5)
- Materials (2)
- Mathematics (2)
- Mercury (2)
- Microscopy (7)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (14)
- National Security (2)
- Neutron Science (32)
- Nuclear Energy (24)
- Physics (15)
- Polymers (5)
- Quantum Science (12)
- Security (3)
- Space Exploration (2)
- Summit (14)
- Transportation (11)
Media Contacts
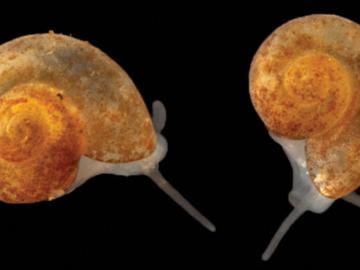
Sometimes conducting big science means discovering a species not much larger than a grain of sand.

As a teenager, Kat Royston had a lot of questions. Then an advanced-placement class in physics convinced her all the answers were out there.
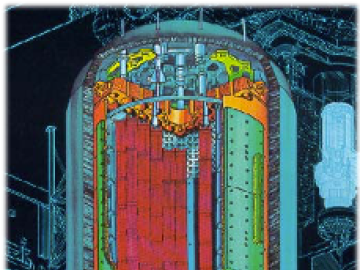
A software package, 10 years in the making, that can predict the behavior of nuclear reactors’ cores with stunning accuracy has been licensed commercially for the first time.

A versatile class of flexible, protein-like polymers could significantly advance future drug delivery methods. But first, scientists have to develop a reliable process for tailoring these polymers into shapes that can effectively transport medicines throughout the human body.

The techniques Theodore Biewer and his colleagues are using to measure whether plasma has the right conditions to create fusion have been around awhile.
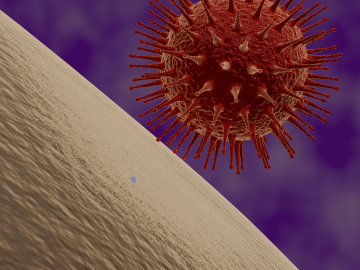
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have used Summit, the world’s most powerful and smartest supercomputer, to identify 77 small-molecule drug compounds that might warrant further study in the fight

Biological membranes, such as the “walls” of most types of living cells, primarily consist of a double layer of lipids, or “lipid bilayer,” that forms the structure, and a variety of embedded and attached proteins with highly specialized functions, including proteins that rapidly and selectively transport ions and molecules in and out of the cell.
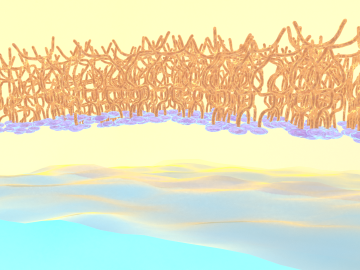
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Feb. 27, 2020 — Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee achieved a rare look at the inner workings of polymer self-assembly at an oil-water interface to advance materials for neuromorphic computing and bio-inspired technologies.

We have a data problem. Humanity is now generating more data than it can handle; more sensors, smartphones, and devices of all types are coming online every day and contributing to the ever-growing global dataset.

Each year, approximately 6 billion gallons of fuel are wasted as vehicles wait at stop lights or sit in dense traffic with engines idling, according to US Department of Energy estimates.


