
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials (52)
- (-) Neutron Science (46)
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (17)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Energy Science (22)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (3)
- Isotopes (5)
- Materials for Computing (5)
- National Security (15)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (16)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (24)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (3)
- (-) Isotopes (8)
- (-) Machine Learning (5)
- (-) Microscopy (13)
- (-) Nanotechnology (26)
- (-) Neutron Science (49)
- (-) Security (3)
- (-) Space Exploration (2)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (12)
- Artificial Intelligence (8)
- Big Data (2)
- Bioenergy (10)
- Biology (5)
- Biomedical (13)
- Buildings (2)
- Chemical Sciences (13)
- Clean Water (1)
- Composites (4)
- Computer Science (14)
- Coronavirus (9)
- Critical Materials (5)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Energy Storage (23)
- Environment (10)
- Exascale Computing (2)
- Frontier (3)
- Fusion (2)
- Grid (3)
- High-Performance Computing (4)
- Materials (26)
- Materials Science (49)
- Mathematics (1)
- Molten Salt (1)
- National Security (4)
- Nuclear Energy (7)
- Partnerships (4)
- Physics (16)
- Polymers (11)
- Quantum Science (7)
- Simulation (1)
- Summit (6)
- Transportation (8)
Media Contacts

Pauling’s Rules is the standard model used to describe atomic arrangements in ordered materials. Neutron scattering experiments at Oak Ridge National Laboratory confirmed this approach can also be used to describe highly disordered materials.

To better understand how the novel coronavirus behaves and how it can be stopped, scientists have completed a three-dimensional map that reveals the location of every atom in an enzyme molecule critical to SARS-CoV-2 reproduction.

An international multi-institution team of scientists has synthesized graphene nanoribbons – ultrathin strips of carbon atoms – on a titanium dioxide surface using an atomically precise method that removes a barrier for custom-designed carbon

Two scientists with the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have been elected fellows of the American Physical Society.

Geoffrey L. Greene, a professor at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, who holds a joint appointment with ORNL, will be awarded the 2021 Tom Bonner Prize for Nuclear Physics from the American Physical Society.

Led by ORNL and the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, a study of a solar-energy material with a bright future revealed a way to slow phonons, the waves that transport heat.
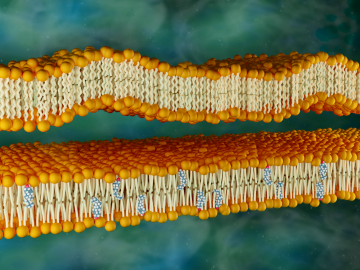
Neutron scattering at ORNL has shown that cholesterol stiffens simple lipid membranes, a finding that may help us better understand the functioning of human cells.
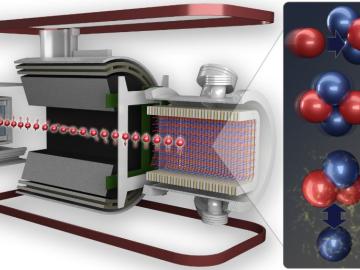
Through a one-of-a-kind experiment at ORNL, nuclear physicists have precisely measured the weak interaction between protons and neutrons. The result quantifies the weak force theory as predicted by the Standard Model of Particle Physics.
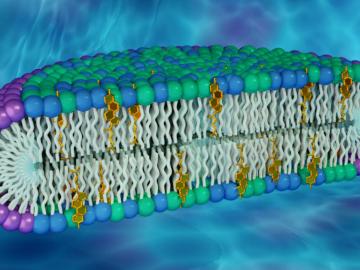
A team of researchers led by Vanderbilt University has recently shed light on how membrane proteins could be influenced by the lipids around them. By developing a novel type of membrane model, the scientists were able to show that the shape and behavior of a protein can be altered by exposure to different lipid compositions.

Researchers at ORNL used quantum optics to advance state-of-the-art microscopy and illuminate a path to detecting material properties with greater sensitivity than is possible with traditional tools.


