
Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (26)
- (-) Fusion (9)
- (-) Isotopes (11)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (21)
- (-) Security (3)
- (-) Transportation (18)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (20)
- Advanced Reactors (3)
- Big Data (10)
- Bioenergy (22)
- Biology (29)
- Biomedical (7)
- Biotechnology (6)
- Buildings (14)
- Chemical Sciences (24)
- Clean Water (5)
- Composites (6)
- Computer Science (23)
- Coronavirus (4)
- Critical Materials (6)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Education (3)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (21)
- Environment (43)
- Exascale Computing (15)
- Fossil Energy (2)
- Frontier (19)
- Grid (16)
- High-Performance Computing (33)
- Hydropower (3)
- Irradiation (2)
- Machine Learning (15)
- Materials (59)
- Materials Science (16)
- Mathematics (2)
- Mercury (2)
- Microelectronics (2)
- Microscopy (7)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (7)
- National Security (21)
- Neutron Science (32)
- Partnerships (24)
- Physics (14)
- Polymers (4)
- Quantum Computing (12)
- Quantum Science (9)
- Simulation (29)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (4)
- Summit (9)
Media Contacts
Roane State Community College today announced the launch of a Nuclear Technology Program with a $100,000 contribution from UT-Battelle, LLC, which manages and operates ORNL for the Department of Energy.

Wildfires have shaped the environment for millennia, but they are increasing in frequency, range and intensity in response to a hotter climate. The phenomenon is being incorporated into high-resolution simulations of the Earth’s climate by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, with a mission to better understand and predict environmental change.

When geoinformatics engineering researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory wanted to better understand changes in land areas and points of interest around the world, they turned to the locals — their data, at least.
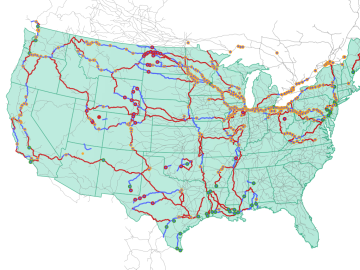
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers used images from a photo-sharing website to identify crude oil train routes across the nation to provide data that could help transportation planners better understand regional impacts.

JungHyun Bae is a nuclear scientist studying applications of particles that have some beneficial properties: They are everywhere, they are unlimited, they are safe.

Creating energy the way the sun and stars do — through nuclear fusion — is one of the grand challenges facing science and technology. What’s easy for the sun and its billions of relatives turns out to be particularly difficult on Earth.

Working with Western Michigan University and other partners, ORNL engineers are placing low-powered sensors in the reflective raised pavement markers that are already used to help drivers identify lanes. Microchips inside the markers transmit information to passing cars about the road shape to help autonomous driving features function even when vehicle cameras or remote laser sensing, called LiDAR, are unreliable because of fog, snow, glare or other obstructions.

To support the development of a revolutionary new open fan engine architecture for the future of flight, GE Aerospace has run simulations using the world’s fastest supercomputer capable of crunching data in excess of exascale speed, or more than a quintillion calculations per second.

Innovations in artificial intelligence are rapidly shaping our world, from virtual assistants and chatbots to self-driving cars and automated manufacturing.

Like most scientists, Chengping Chai is not content with the surface of things: He wants to probe beyond to learn what’s really going on. But in his case, he is literally building a map of the world beneath, using seismic and acoustic data that reveal when and where the earth moves.


