
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (11)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (5)
- Energy Science (14)
- Fusion and Fission (5)
- Fusion Energy (7)
- Isotopes (20)
- Materials (17)
- Materials for Computing (2)
- National Security (11)
- Neutron Science (11)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (13)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (7)
- Supercomputing (63)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (25)
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (92)
- (-) Isotopes (38)
- (-) Quantum Science (59)
- (-) Security (17)
- (-) Space Exploration (23)
- (-) Summit (48)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (89)
- Big Data (62)
- Bioenergy (84)
- Biology (100)
- Biomedical (53)
- Biotechnology (28)
- Buildings (50)
- Chemical Sciences (48)
- Clean Water (30)
- Composites (21)
- Computer Science (153)
- Coronavirus (30)
- Critical Materials (17)
- Cybersecurity (17)
- Education (2)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (64)
- Environment (164)
- Exascale Computing (52)
- Fossil Energy (7)
- Frontier (45)
- Fusion (47)
- Grid (54)
- High-Performance Computing (93)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (51)
- Materials (87)
- Materials Science (89)
- Mathematics (11)
- Mercury (10)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (34)
- Molten Salt (7)
- Nanotechnology (29)
- National Security (63)
- Neutron Science (109)
- Nuclear Energy (85)
- Partnerships (37)
- Physics (38)
- Polymers (18)
- Quantum Computing (39)
- Simulation (51)
- Software (1)
- Statistics (3)
- Transportation (66)
Media Contacts

A team of researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Purdue University has taken an important step toward this goal by harnessing the frequency, or color, of light. Such capabilities could contribute to more practical and large-scale quantum networks exponentially more powerful and secure than the classical networks we have today.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists demonstrated that an electron microscope can be used to selectively remove carbon atoms from graphene’s atomically thin lattice and stitch transition-metal dopant atoms in their place.

Twenty-seven ORNL researchers Zoomed into 11 middle schools across Tennessee during the annual Engineers Week in February. East Tennessee schools throughout Oak Ridge and Roane, Sevier, Blount and Loudon counties participated, with three West Tennessee schools joining in.
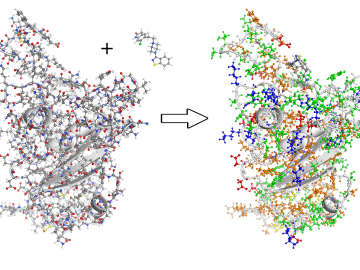
To better understand the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have harnessed the power of supercomputers to accurately model the spike protein that binds the novel coronavirus to a human cell receptor.

On Feb. 18, the world will be watching as NASA’s Perseverance rover makes its final descent into Jezero Crater on the surface of Mars. Mars 2020 is the first NASA mission that uses plutonium-238 produced at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

A better way of welding targets for Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s plutonium-238 production has sped up the process and improved consistency and efficiency. This advancement will ultimately benefit the lab’s goal to make enough Pu-238 – the isotope that powers NASA’s deep space missions – to yield 1.5 kilograms of plutonium oxide annually by 2026.

Since the 1930s, scientists have been using particle accelerators to gain insights into the structure of matter and the laws of physics that govern our world.

Algorithms developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory can greatly enhance X-ray computed tomography images of 3D-printed metal parts, resulting in more accurate, faster scans.

Porter Bailey started and will end his 33-year career at ORNL in the same building: 7920 of the Radiochemical Engineering Development Center.

East Tennessee occupies a special place in nuclear history. In 1943, the world’s first continuously operating reactor began operating on land that would become ORNL.


