
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) National Security (29)
- (-) Supercomputing (58)
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (93)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (6)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Science (95)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (25)
- Fusion Energy (15)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (42)
- Materials for Computing (4)
- Mathematics (1)
- Neutron Science (17)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (14)
- Quantum information Science (9)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Cybersecurity (23)
- (-) Environment (26)
- (-) Fusion (2)
- (-) Grid (11)
- (-) Molten Salt (1)
- (-) Quantum Science (26)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (7)
- Advanced Reactors (2)
- Artificial Intelligence (46)
- Big Data (25)
- Bioenergy (11)
- Biology (14)
- Biomedical (17)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (4)
- Chemical Sciences (5)
- Computer Science (104)
- Coronavirus (16)
- Critical Materials (3)
- Energy Storage (9)
- Exascale Computing (26)
- Frontier (32)
- High-Performance Computing (45)
- Isotopes (2)
- Machine Learning (24)
- Materials (16)
- Materials Science (17)
- Mathematics (2)
- Microscopy (7)
- Nanotechnology (11)
- National Security (35)
- Neutron Science (15)
- Nuclear Energy (8)
- Partnerships (5)
- Physics (9)
- Polymers (2)
- Quantum Computing (20)
- Security (15)
- Simulation (16)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (3)
- Summit (43)
- Transportation (8)
Media Contacts
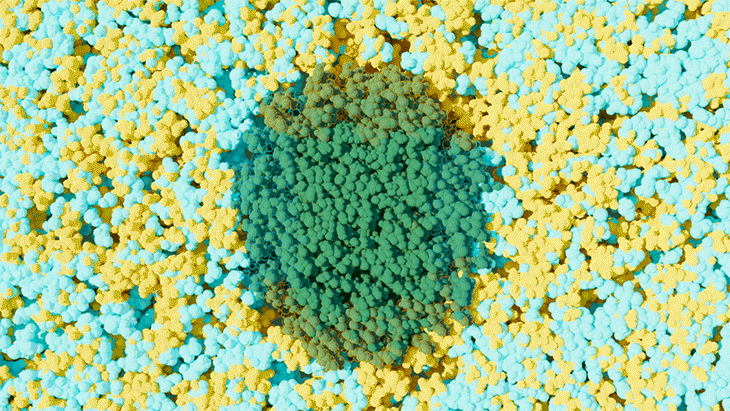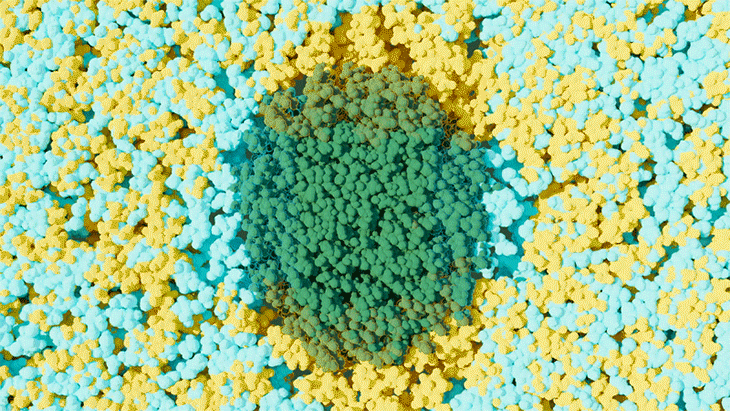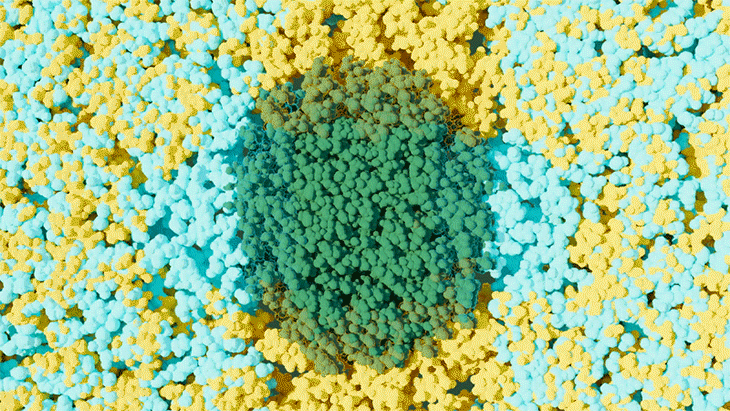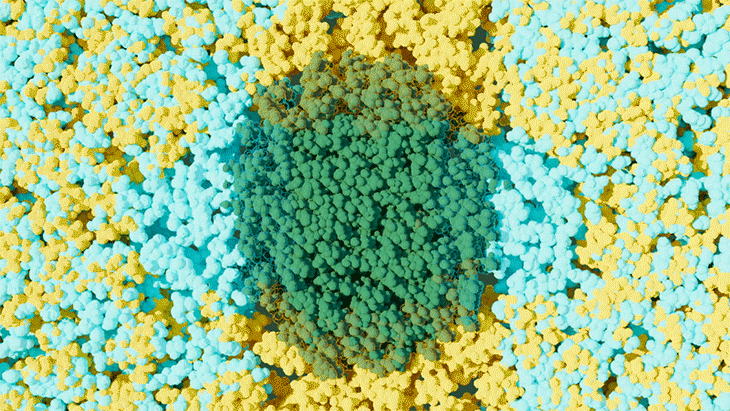
Scientists at ORNL used neutron scattering and supercomputing to better understand how an organic solvent and water work together to break down plant biomass, creating a pathway to significantly improve the production of renewable

Scientists from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and a dozen other international research institutions have produced the most elaborate set of projections to date that illustrates possible futures for major monsoon regions.

For the second year in a row, a team from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge and Los Alamos national laboratories led a demonstration hosted by EPB, a community-based utility and telecommunications company serving Chattanooga, Tennessee.
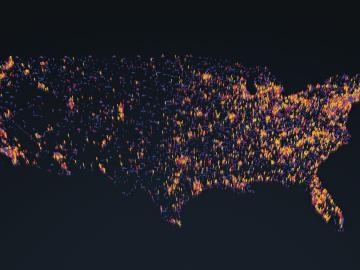
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., May 5, 2020 — By 2050, the United States will likely be exposed to a larger number of extreme climate events, including more frequent heat waves, longer droughts and more intense floods, which can lead to greater risks for human health, ecosystem stability and regional economies.
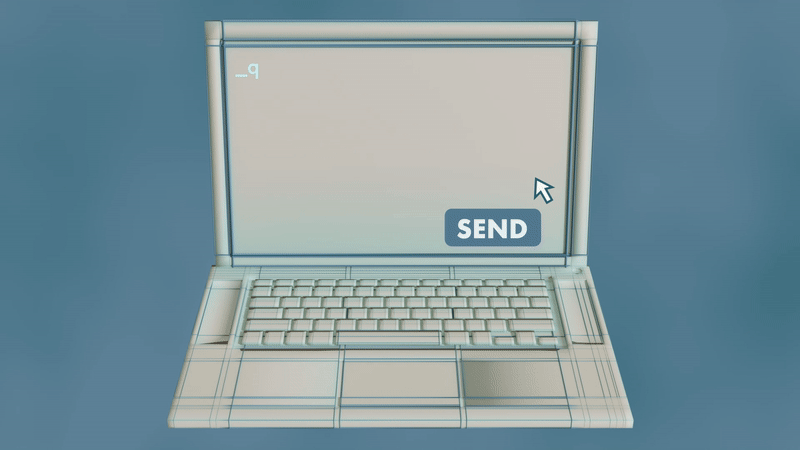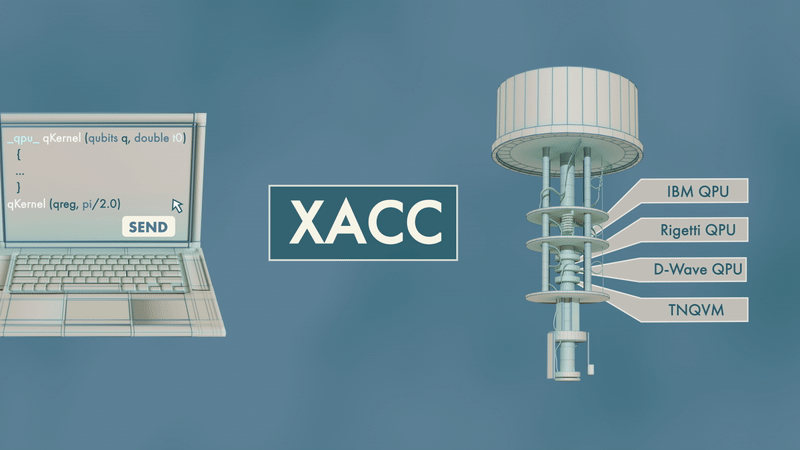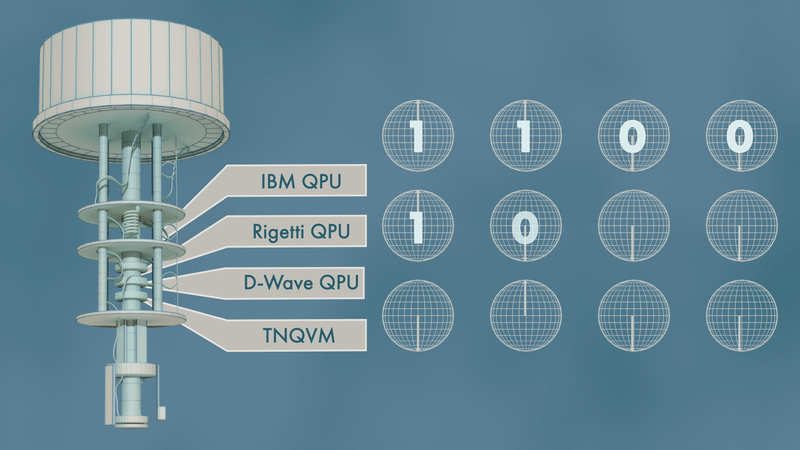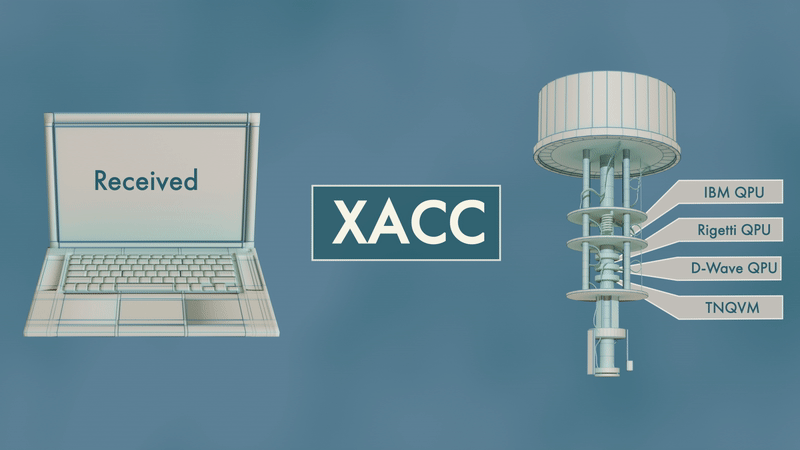
In the early 2000s, high-performance computing experts repurposed GPUs — common video game console components used to speed up image rendering and other time-consuming tasks

We have a data problem. Humanity is now generating more data than it can handle; more sensors, smartphones, and devices of all types are coming online every day and contributing to the ever-growing global dataset.

A novel approach developed by scientists at ORNL can scan massive datasets of large-scale satellite images to more accurately map infrastructure – such as buildings and roads – in hours versus days.

The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

A team from the ORNL has conducted a series of experiments to gain a better understanding of quantum mechanics and pursue advances in quantum networking and quantum computing, which could lead to practical applications in cybersecurity and other areas.

To better determine the potential energy cost savings among connected homes, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a computer simulation to more accurately compare energy use on similar weather days.


