
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Energy Science (105)
- (-) Fusion Energy (6)
- (-) Supercomputing (46)
- Advanced Manufacturing (14)
- Biology and Environment (85)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (8)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (2)
- Fusion and Fission (6)
- Materials (22)
- Materials for Computing (4)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (20)
- Neutron Science (11)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (12)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (7)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (47)
- (-) Advanced Reactors (9)
- (-) Environment (46)
- (-) Grid (28)
- (-) Machine Learning (11)
- (-) Quantum Science (15)
- Artificial Intelligence (25)
- Big Data (21)
- Bioenergy (14)
- Biology (12)
- Biomedical (14)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (25)
- Chemical Sciences (6)
- Clean Water (7)
- Composites (11)
- Computer Science (73)
- Coronavirus (16)
- Critical Materials (7)
- Cybersecurity (7)
- Energy Storage (42)
- Exascale Computing (17)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (18)
- Fusion (11)
- High-Performance Computing (28)
- Hydropower (3)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (23)
- Materials Science (24)
- Mathematics (4)
- Mercury (2)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (6)
- Nanotechnology (8)
- National Security (4)
- Neutron Science (8)
- Nuclear Energy (15)
- Partnerships (4)
- Physics (4)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (15)
- Security (4)
- Simulation (14)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (5)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (29)
- Transportation (46)
Media Contacts
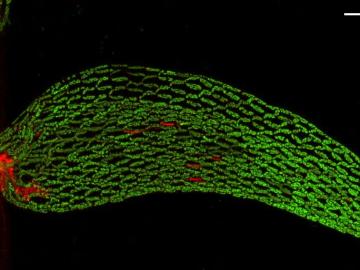
A team of scientists found that critical interactions between microbes and peat moss break down under warming temperatures, impacting moss health and ultimately carbon stored in soil.
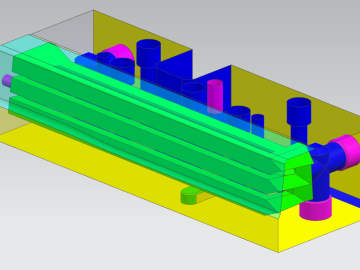
Researchers demonstrated that an additively manufactured hot stamping die can withstand up to 25,000 usage cycles, proving that this technique is a viable solution for production.

Elizabeth Herndon believes in going the distance whether she is preparing to compete in the 2020 Olympic marathon trials or examining how metals move through the environment as a geochemist at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

In the vast frozen whiteness of the central Arctic, the Polarstern, a German research vessel, has settled into the ice for a yearlong float.

In a recent study, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory performed experiments in a prototype fusion reactor materials testing facility to develop a method that uses microwaves to raise the plasma’s temperature closer to the extreme values

A team including Oak Ridge National Laboratory and University of Tennessee researchers demonstrated a novel 3D printing approach called Z-pinning that can increase the material’s strength and toughness by more than three and a half times compared to conventional additive manufacturing processes.

Isabelle Snyder calls faults as she sees them, whether it’s modeling operations for the nation’s power grid or officiating at the US Open Tennis Championships.

Using additive manufacturing, scientists experimenting with tungsten at Oak Ridge National Laboratory hope to unlock new potential of the high-performance heat-transferring material used to protect components from the plasma inside a fusion reactor. Fusion requires hydrogen isotopes to reach millions of degrees.
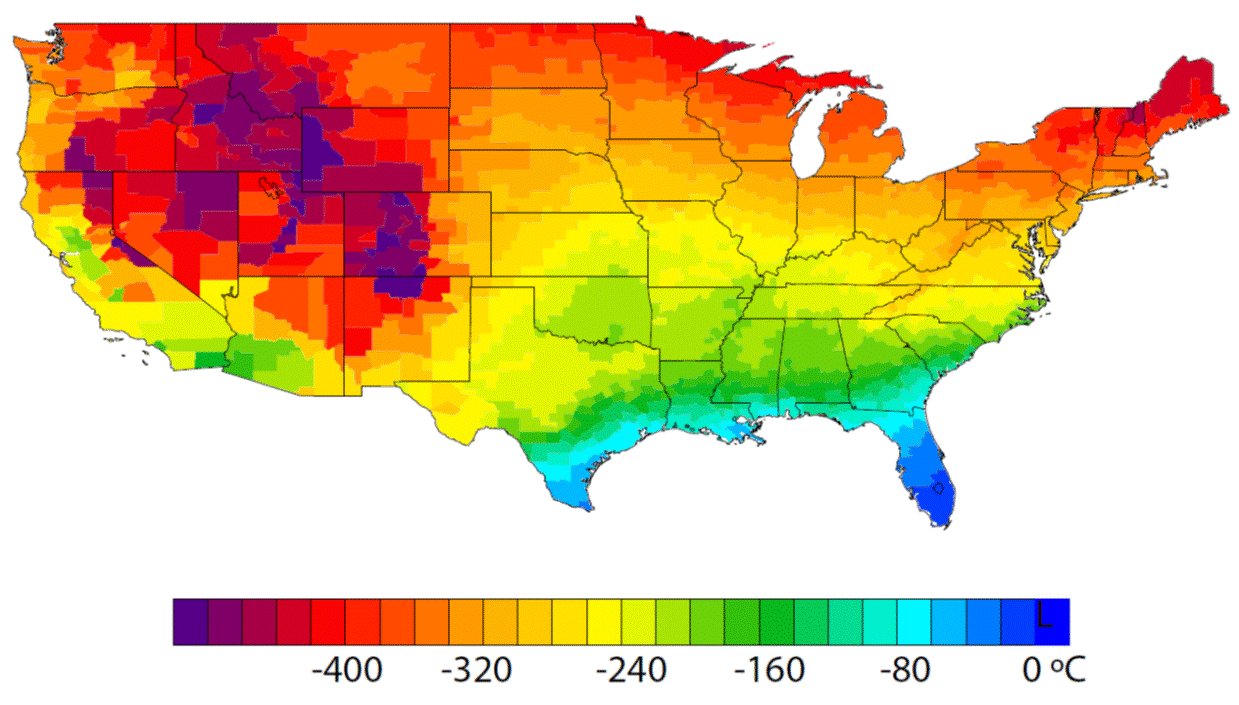
A detailed study by Oak Ridge National Laboratory estimated how much more—or less—energy United States residents might consume by 2050 relative to predicted shifts in seasonal weather patterns

In the shifting landscape of global manufacturing, American ingenuity is once again giving U.S companies an edge with radical productivity improvements as a result of advanced materials and robotic systems developed at the Department of Energy’s Manufacturing Demonstration Facility (MDF) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory.


