
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials (54)
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (53)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (12)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (2)
- Energy Science (102)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fusion and Fission (7)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotopes (5)
- Materials for Computing (13)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (17)
- Neutron Science (21)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Quantum information Science (6)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (94)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Biomedical (4)
- (-) Computer Science (9)
- (-) Grid (2)
- (-) Nanotechnology (16)
- (-) Physics (12)
- (-) Polymers (10)
- (-) Summit (1)
- (-) Transportation (10)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (10)
- Advanced Reactors (2)
- Artificial Intelligence (4)
- Big Data (2)
- Bioenergy (3)
- Buildings (2)
- Chemical Sciences (11)
- Clean Water (3)
- Composites (6)
- Coronavirus (2)
- Critical Materials (5)
- Cybersecurity (1)
- Energy Storage (13)
- Environment (7)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fusion (4)
- High-Performance Computing (1)
- Isotopes (8)
- Machine Learning (2)
- Materials (31)
- Materials Science (36)
- Mathematics (1)
- Microscopy (12)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Neutron Science (13)
- Nuclear Energy (12)
- Partnerships (3)
- Quantum Computing (2)
- Quantum Science (1)
- Security (1)
- Space Exploration (2)
Media Contacts

A new method developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory improves the energy efficiency of a desalination process known as solar-thermal evaporation.
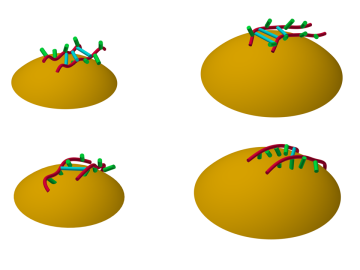
A team of researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated that designed synthetic polymers can serve as a high-performance binding material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.
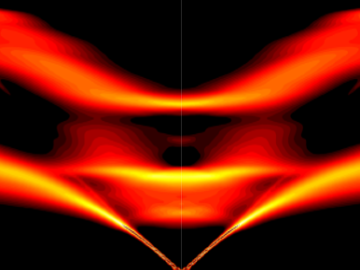
Scientists have discovered a way to alter heat transport in thermoelectric materials, a finding that may ultimately improve energy efficiency as the materials

Ionic conduction involves the movement of ions from one location to another inside a material. The ions travel through point defects, which are irregularities in the otherwise consistent arrangement of atoms known as the crystal lattice. This sometimes sluggish process can limit the performance and efficiency of fuel cells, batteries, and other energy storage technologies.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists studying fuel cells as a potential alternative to internal combustion engines used sophisticated electron microscopy to investigate the benefits of replacing high-cost platinum with a lower cost, carbon-nitrogen-manganese-based catalyst.

Carbon fiber composites—lightweight and strong—are great structural materials for automobiles, aircraft and other transportation vehicles. They consist of a polymer matrix, such as epoxy, into which reinforcing carbon fibers have been embedded. Because of differences in the mecha...
Physicists turned to the “doubly magic” tin isotope Sn-132, colliding it with a target at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to assess its properties as it lost a neutron to become Sn-131.

An Oak Ridge National Laboratory-led team used a scanning transmission electron microscope to selectively position single atoms below a crystal’s surface for the first time.

A new microscopy technique developed at the University of Illinois at Chicago allows researchers to visualize liquids at the nanoscale level — about 10 times more resolution than with traditional transmission electron microscopy — for the first time. By trapping minute amounts of...
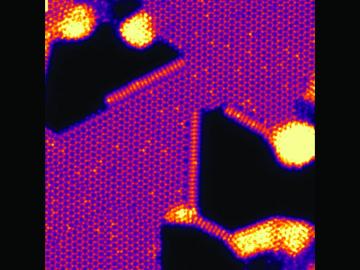
An Oak Ridge National Laboratory–led team has learned how to engineer tiny pores embellished with distinct edge structures inside atomically-thin two-dimensional, or 2D, crystals. The 2D crystals are envisioned as stackable building blocks for ultrathin electronics and other advance...


