
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biology and Environment (80)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (3)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (2)
- Energy Science (72)
- Fusion and Fission (19)
- Fusion Energy (11)
- Isotopes (19)
- Materials (56)
- Materials for Computing (10)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (21)
- Neutron Science (79)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (13)
- Quantum information Science (2)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (44)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Clean Water (30)
- (-) Cybersecurity (17)
- (-) Environment (164)
- (-) Fusion (47)
- (-) Grid (54)
- (-) Isotopes (38)
- (-) Nanotechnology (29)
- (-) Neutron Science (109)
- (-) Partnerships (37)
- (-) Physics (38)
- (-) Simulation (51)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (89)
- Advanced Reactors (25)
- Artificial Intelligence (92)
- Big Data (62)
- Bioenergy (84)
- Biology (100)
- Biomedical (53)
- Biotechnology (28)
- Buildings (50)
- Chemical Sciences (48)
- Composites (21)
- Computer Science (153)
- Coronavirus (30)
- Critical Materials (17)
- Education (2)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (64)
- Exascale Computing (52)
- Fossil Energy (7)
- Frontier (45)
- High-Performance Computing (93)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (2)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (51)
- Materials (87)
- Materials Science (89)
- Mathematics (11)
- Mercury (10)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (34)
- Molten Salt (7)
- National Security (63)
- Nuclear Energy (85)
- Polymers (18)
- Quantum Computing (39)
- Quantum Science (58)
- Security (17)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (23)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (48)
- Transportation (66)
Media Contacts

The inside of future nuclear fusion energy reactors will be among the harshest environments ever produced on Earth. What’s strong enough to protect the inside of a fusion reactor from plasma-produced heat fluxes akin to space shuttles reentering Earth’s atmosphere?
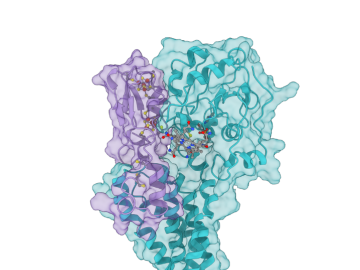
A team led by ORNL created a computational model of the proteins responsible for the transformation of mercury to toxic methylmercury, marking a step forward in understanding how the reaction occurs and how mercury cycles through the environment.

Pick your poison. It can be deadly for good reasons such as protecting crops from harmful insects or fighting parasite infection as medicine — or for evil as a weapon for bioterrorism. Or, in extremely diluted amounts, it can be used to enhance beauty.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists evaluating northern peatland responses to environmental change recorded extraordinary fine-root growth with increasing temperatures, indicating that this previously hidden belowground mechanism may play an important role in how carbon-rich peatlands respond to warming.

A UCLA-led team that discovered the first intrinsic ferromagnetic topological insulator – a quantum material that could revolutionize next-generation electronics – used neutrons at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to help verify their finding.
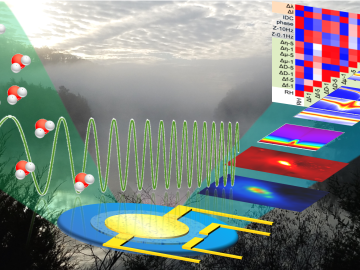
An all-in-one experimental platform developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences accelerates research on promising materials for future technologies.

Combining expertise in physics, applied math and computing, Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists are expanding the possibilities for simulating electromagnetic fields that underpin phenomena in materials design and telecommunications.

The 75th anniversary of the final voyage of the USS Indianapolis and her brave crew is Thursday, July 30. The US Navy warship was on a top-secret mission across the Pacific Ocean to deliver war materials that marked the conclusion of the Manhattan Project.

ORNL researchers have developed an intelligent power electronic inverter platform that can connect locally sited energy resources such as solar panels, energy storage and electric vehicles and smoothly interact with the utility power grid.

Lithium, the silvery metal that powers smart phones and helps treat bipolar disorders, could also play a significant role in the worldwide effort to harvest on Earth the safe, clean and virtually limitless fusion energy that powers the sun and stars.


