
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (33)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Energy Science (46)
- Fusion and Fission (8)
- Isotopes (17)
- Materials (27)
- Materials for Computing (5)
- National Security (17)
- Neutron Science (57)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (7)
- Supercomputing (41)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (12)
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (77)
- (-) Clean Water (16)
- (-) Composites (11)
- (-) Cybersecurity (14)
- (-) Isotopes (33)
- (-) Neutron Science (82)
- (-) Security (16)
- (-) Simulation (42)
- (-) Space Exploration (13)
- (-) Transportation (30)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (56)
- Big Data (45)
- Bioenergy (68)
- Biology (80)
- Biomedical (42)
- Biotechnology (25)
- Buildings (30)
- Chemical Sciences (35)
- Computer Science (111)
- Coronavirus (19)
- Critical Materials (5)
- Education (2)
- Emergency (3)
- Energy Storage (32)
- Environment (116)
- Exascale Computing (51)
- Fossil Energy (6)
- Frontier (44)
- Fusion (38)
- Grid (32)
- High-Performance Computing (81)
- Hydropower (6)
- ITER (4)
- Machine Learning (37)
- Materials (51)
- Materials Science (55)
- Mathematics (8)
- Mercury (7)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (23)
- Molten Salt (2)
- Nanotechnology (17)
- National Security (60)
- Nuclear Energy (66)
- Partnerships (36)
- Physics (34)
- Polymers (9)
- Quantum Computing (35)
- Quantum Science (48)
- Software (1)
- Statistics (2)
- Summit (40)
Media Contacts

To support the development of a revolutionary new open fan engine architecture for the future of flight, GE Aerospace has run simulations using the world’s fastest supercomputer capable of crunching data in excess of exascale speed, or more than a quintillion calculations per second.
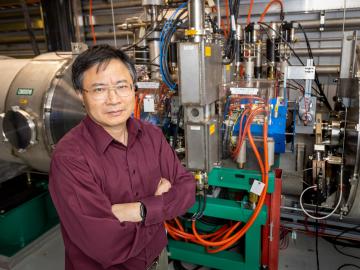
When opportunity meets talent, great things happen. The laser comb developed at ORNL serves as such an example.

Having passed the midpoint of his career, physicist Mali Balasubramanian was part of a tight-knit team at a premier research facility for X-ray spectroscopy. But then another position opened, at ORNL— one that would take him in a new direction.

When reading the novel Jurassic Park as a teenager, Jerry Parks found the passages about gene sequencing and supercomputers fascinating, but never imagined he might someday pursue such futuristic-sounding science.

A study led by researchers at ORNL could uncover new ways to produce more powerful, longer-lasting batteries and memory devices.

Nature-based solutions are an effective tool to combat climate change triggered by rising carbon emissions, whether it’s by clearing the skies with bio-based aviation fuels or boosting natural carbon sinks.

As renewable sources of energy such as wind and sun power are being increasingly added to the country’s electrical grid, old-fashioned nuclear energy is also being primed for a resurgence.

As a biogeochemist at ORNL, Matthew Berens studies how carbon, nutrients and minerals move through water and soil. In this firsthand account, Berens describes recent fieldwork in Louisiana with colleagues.

Inspired by one of the mysteries of human perception, an ORNL researcher invented a new way to hide sensitive electric grid information from cyberattack: within a constantly changing color palette.

Growing up in suburban Upper East Tennessee, Layla Marshall didn’t see a lot of STEM opportunities for children.
“I like encouraging young people to get involved in the kinds of things I’ve been doing in my career,” said Marshall. “I like seeing the students achieve their goals. It’s fun to watch them get excited about learning new things and teaching the robot to do things that they didn’t know it could do until they tried it.”
Marshall herself has a passion for learning new things.


