
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (19)
- Biology and Environment (21)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (8)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (2)
- Energy Science (123)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (7)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials (46)
- Materials for Computing (10)
- National Security (14)
- Neutron Science (15)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (12)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (34)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (93)
- (-) Advanced Reactors (27)
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (62)
- (-) Biomedical (32)
- (-) Composites (25)
- (-) Grid (43)
- (-) Molten Salt (8)
- (-) Polymers (24)
- (-) Transportation (73)
- Big Data (34)
- Bioenergy (46)
- Biology (51)
- Biotechnology (16)
- Buildings (43)
- Chemical Sciences (57)
- Clean Water (16)
- Computer Science (121)
- Coronavirus (28)
- Critical Materials (23)
- Cybersecurity (21)
- Education (3)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (80)
- Environment (99)
- Exascale Computing (24)
- Fossil Energy (2)
- Frontier (25)
- Fusion (28)
- High-Performance Computing (58)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (29)
- ITER (6)
- Machine Learning (31)
- Materials (107)
- Materials Science (94)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (5)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (31)
- Nanotechnology (44)
- National Security (26)
- Neutron Science (88)
- Nuclear Energy (55)
- Partnerships (36)
- Physics (31)
- Quantum Computing (21)
- Quantum Science (46)
- Security (13)
- Simulation (24)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (13)
- Statistics (2)
- Summit (32)
Media Contacts
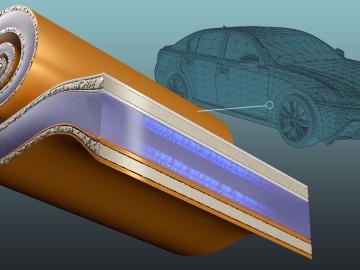
Strengthening the competitiveness of the U.S. transportation industry depends on developing domestic EV batteries that combine rapid charging with long-range performance — two goals that often conflict. Researchers at ORNL have addressed this challenge by redesigning a key battery component, enabling fast, 10-minute charging while improving energy density and reducing reliance on copper.
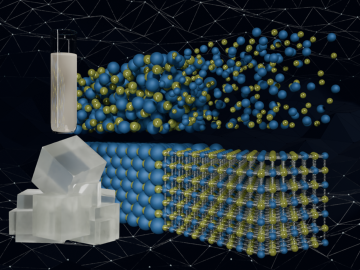
Scientists have developed a new machine learning approach that accurately predicted critical and difficult-to-compute properties of molten salts, materials with diverse nuclear energy applications.

Researchers at ORNL have developed an innovative new technique using carbon nanofibers to enhance binding in carbon fiber and other fiber-reinforced polymer composites – an advance likely to improve structural materials for automobiles, airplanes and other applications that require lightweight and strong materials.

Researchers at ORNL have developed a tool that gives builders a quick way to measure, correct and certify level foundations. FLAT, or the Flat and Level Analysis Tool, examines a 360-degree laser scan of a construction site using ORNL-developed segmentation algorithms and machine learning to locate uneven areas on a concrete slab.

Recent advancements at ORNL show that 3D-printed metal molds offer a faster, more cost-effective and flexible approach to producing large composite components for mass-produced vehicles than traditional tooling methods.

Scientists at ORNL have developed a vacuum-assisted extrusion method that reduces internal porosity by up to 75% in large-scale 3D-printed polymer parts. This new technique addresses the critical issue of porosity in large-scale prints but also paves the way for stronger composites.

Research teams at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory received computing resource awards to train and test AI foundation models for science. A total of six ORNL projects were awarded allocations from the National Artificial Intelligence Research Resource, or NAIRR, pilot and the Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment, or INCITE, program to train their AI models.
Mariam Kiran, a quantum research scientist at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was recently honored as a finalist at the British Council’s Study U.K. Alumni Awards 2025, which celebrate the achievements of U.K. alumni worldwide.
Daniel Jacobson, distinguished research scientist in the Biosciences Division at ORNL, has been elected a Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering, or AIMBE, for his achievements in computational biology.
Scientists at ORNL have developed a method that can track chemical changes in molten salt in real time — helping to pave the way for the deployment of molten salt reactors for energy production.


