
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (15)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (6)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Science (45)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (2)
- Fusion and Fission (15)
- Fusion Energy (8)
- Isotopes (5)
- Materials (45)
- Materials for Computing (7)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (5)
- Neutron Science (34)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (15)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Supercomputing (19)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (33)
- (-) Biomedical (18)
- (-) Clean Water (14)
- (-) Energy Storage (50)
- (-) Fusion (19)
- (-) Nanotechnology (25)
- (-) Neutron Science (42)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (36)
- (-) Software (1)
- (-) Space Exploration (11)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (57)
- Advanced Reactors (18)
- Big Data (26)
- Bioenergy (26)
- Biology (31)
- Biotechnology (6)
- Buildings (31)
- Chemical Sciences (31)
- Composites (16)
- Computer Science (70)
- Coronavirus (15)
- Critical Materials (13)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Emergency (2)
- Environment (67)
- Exascale Computing (11)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (10)
- Grid (28)
- High-Performance Computing (33)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (15)
- ITER (5)
- Machine Learning (19)
- Materials (70)
- Materials Science (54)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (3)
- Microscopy (21)
- Molten Salt (6)
- National Security (13)
- Partnerships (11)
- Physics (11)
- Polymers (15)
- Quantum Computing (9)
- Quantum Science (17)
- Security (4)
- Simulation (16)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (11)
- Transportation (52)
Media Contacts

Researchers have identified a molecule essential for the microbial conversion of inorganic mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury, moving closer to blocking the dangerous pollutant before it forms.

Researchers used the world’s fastest supercomputer, Frontier, to train an AI model that designs proteins, with applications in fields like vaccines, cancer treatments, and environmental bioremediation. The study earned a finalist nomination for the Gordon Bell Prize, recognizing innovation in high-performance computing for science.

Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory used the Frontier supercomputer to train the world’s largest AI model for weather prediction, paving the way for hyperlocal, ultra-accurate forecasts. This achievement earned them a finalist nomination for the prestigious Gordon Bell Prize for Climate Modeling.

Scientists at ORNL are studying the failure mechanisms of a new solid electrolyte battery to enhance long-term storage for renewable energy, aiming to make wind and solar power more reliable for the electric grid.

A team of researchers used the Frontier supercomputer and a new methodology for conducting a genome-wide association study to earn a finalist nomination for the Association for Computing Machinery’s 2024 Gordon Bell Prize for outstanding

Kathryn McCarthy, director of the US ITER Project at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been awarded the 2024 E. Gail de Planque Medal by the American Nuclear Society.
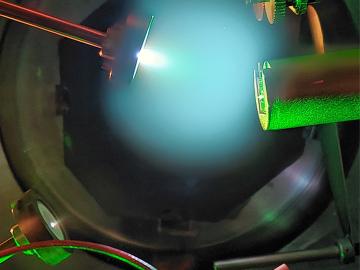
In a game-changing study, ORNL scientists developed a deep learning model — a type of artificial intelligence that mimics human brain function — to analyze high-speed videos of plasma plumes during a process called pulsed laser deposition.

ORNL’s Matthew Loyd will receive a Department of Energy Office of Science Early Career Research award.

A research scientist with the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Ayana Ghosh was named the 2024 Early Discovery Award winner by the American Ceramic Society. The award recognizes an early career member of the organization who has contributed to basic science in the field of glass and ceramics.

The award was given in “recognition of his lifelong leadership in fusion technology for plasma fueling systems in magnetically confined fusion systems.”


