
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (9)
- Biology and Environment (26)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (3)
- Energy Science (98)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fusion and Fission (7)
- Fusion Energy (3)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials (83)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (14)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- National Security (7)
- Neutron Science (27)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (4)
- Supercomputing (25)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Biomedical (28)
- (-) Chemical Sciences (48)
- (-) Fossil Energy (2)
- (-) Materials Science (90)
- (-) Transportation (62)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (82)
- Advanced Reactors (25)
- Artificial Intelligence (51)
- Big Data (25)
- Bioenergy (42)
- Biology (47)
- Biotechnology (14)
- Buildings (36)
- Clean Water (16)
- Composites (23)
- Computer Science (105)
- Coronavirus (28)
- Critical Materials (23)
- Cybersecurity (20)
- Education (3)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (75)
- Environment (86)
- Exascale Computing (14)
- Frontier (17)
- Fusion (26)
- Grid (38)
- High-Performance Computing (44)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (25)
- ITER (5)
- Machine Learning (27)
- Materials (96)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (5)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (28)
- Molten Salt (8)
- Nanotechnology (41)
- National Security (21)
- Neutron Science (81)
- Nuclear Energy (47)
- Partnerships (33)
- Physics (30)
- Polymers (23)
- Quantum Computing (18)
- Quantum Science (43)
- Security (13)
- Simulation (19)
- Space Exploration (13)
- Statistics (2)
- Summit (30)
Media Contacts
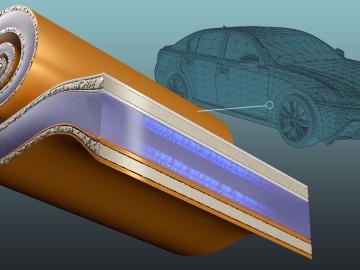
Strengthening the competitiveness of the U.S. transportation industry depends on developing domestic EV batteries that combine rapid charging with long-range performance — two goals that often conflict. Researchers at ORNL have addressed this challenge by redesigning a key battery component, enabling fast, 10-minute charging while improving energy density and reducing reliance on copper.
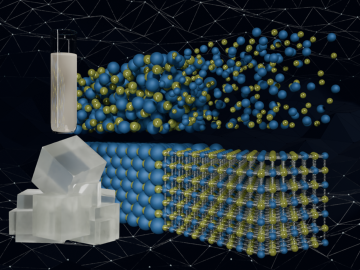
Scientists have developed a new machine learning approach that accurately predicted critical and difficult-to-compute properties of molten salts, materials with diverse nuclear energy applications.

Researchers at ORNL have developed an innovative new technique using carbon nanofibers to enhance binding in carbon fiber and other fiber-reinforced polymer composites – an advance likely to improve structural materials for automobiles, airplanes and other applications that require lightweight and strong materials.

Working at nanoscale dimensions, billionths of a meter in size, a team of scientists led by ORNL revealed a new way to measure high-speed fluctuations in magnetic materials. Knowledge obtained by these new measurements could be used to advance technologies ranging from traditional computing to the emerging field of quantum computing.

By editing the polymers of discarded plastics, ORNL chemists have found a way to generate new macromolecules with more valuable properties than those of the starting material.

P&G is using simulations on the ORNL Summit supercomputer to study how surfactants in cleaners cause eye irritation. By modeling the corneal epithelium, P&G aims to develop safer, concentrated cleaning products that meet performance and safety standards while supporting sustainability goals.

A chemical reaction can convert two polluting greenhouse gases into valuable building blocks for cleaner fuels and feedstocks, but the high temperature required for the reaction also deactivates the catalyst. A team led by ORNL has found a way to thwart deactivation. The strategy may apply broadly to other catalysts.

Researchers have identified a molecule essential for the microbial conversion of inorganic mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury, moving closer to blocking the dangerous pollutant before it forms.

A study led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory details how artificial intelligence researchers created an AI model to help identify new alloys used as shielding for housing fusion applications components in a nuclear reactor. The findings mark a major step towards improving nuclear fusion facilities.

ORNL has partnered with Western Michigan University to advance intelligent road infrastructure through the development of new chip-enabled raised pavement markers. These innovative markers transmit lane-keeping information to passing vehicles, enhancing safety and enabling smarter driving in all weather conditions.


