
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (4)
- Computer Science (1)
- Energy Science (13)
- Fusion and Fission (3)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Materials (24)
- Materials for Computing (4)
- National Security (11)
- Neutron Science (9)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (20)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (12)
- (-) Clean Water (2)
- (-) Cybersecurity (17)
- (-) Frontier (16)
- (-) Physics (26)
- (-) Polymers (13)
- (-) Statistics (1)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (48)
- Artificial Intelligence (35)
- Big Data (8)
- Bioenergy (25)
- Biology (26)
- Biomedical (17)
- Biotechnology (10)
- Buildings (15)
- Chemical Sciences (35)
- Composites (12)
- Computer Science (63)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Critical Materials (11)
- Education (3)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (43)
- Environment (38)
- Exascale Computing (13)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Fusion (17)
- Grid (16)
- High-Performance Computing (32)
- Isotopes (20)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (13)
- Materials (60)
- Materials Science (56)
- Mercury (2)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (17)
- Molten Salt (3)
- Nanotechnology (29)
- National Security (18)
- Neutron Science (54)
- Nuclear Energy (28)
- Partnerships (31)
- Quantum Computing (13)
- Quantum Science (31)
- Security (12)
- Simulation (10)
- Space Exploration (3)
- Summit (22)
- Transportation (26)
Media Contacts

An ORNL-led team's observation of certain crystalline ice phases challenges accepted theories about super-cooled water and non-crystalline ice. Their findings, reported in the journal Nature, will also lead to better understanding of ice and its various phases found on other planets, moons and elsewhere in space.

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., May 7, 2019—The U.S. Department of Energy today announced a contract with Cray Inc. to build the Frontier supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which is anticipated to debut in 2021 as the world’s most powerful computer with a performance of greater than 1.5 exaflops.

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., March 11, 2019—An international collaboration including scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory solved a 50-year-old puzzle that explains why beta decays of atomic nuclei
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Feb. 12, 2019—A team of researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge and Los Alamos National Laboratories has partnered with EPB, a Chattanooga utility and telecommunications company, to demonstrate the effectiveness of metro-scale quantum key distribution (QKD).

The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory is collaborating with industry on six new projects focused on advancing commercial nuclear energy technologies that offer potential improvements to current nuclear reactors and move new reactor designs closer to deployment.

A team of scientists has for the first time measured the elusive weak interaction between protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. They had chosen the simplest nucleus consisting of one neutron and one proton for the study.
Three researchers from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have been elected fellows of the American Physical Society (APS). Fellows of the APS are recognized for their exceptional contributions to the physics enterprise in outstanding resear...
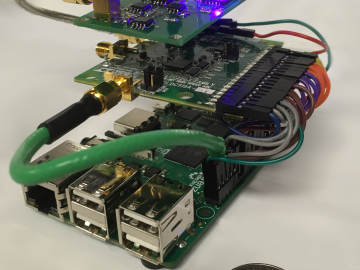
Qrypt, Inc., has exclusively licensed a novel cyber security technology from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, promising a stronger defense against cyberattacks including those posed by quantum computing.

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are the first to successfully simulate an atomic nucleus using a quantum computer. The results, published in Physical Review Letters, demonstrate the ability of quantum systems to compute nuclear ph...

After more than a year of operation at the Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), the COHERENT experiment, using the world’s smallest neutrino detector, has found a big fingerprint of the elusive, electrically neutral particles that interact only weakly with matter.


