
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials Under Extremes (1)
- (-) Neutron Science (20)
- (-) Supercomputing (31)
- Advanced Manufacturing (4)
- Biology and Environment (18)
- Computer Science (2)
- Energy Science (70)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (11)
- Materials (74)
- Materials Characterization (2)
- Materials for Computing (12)
- National Security (4)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (6)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Coronavirus (10)
- (-) Energy Storage (10)
- (-) Frontier (14)
- (-) Isotopes (1)
- (-) Materials (18)
- (-) Space Exploration (3)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Advanced Reactors (1)
- Artificial Intelligence (15)
- Big Data (6)
- Bioenergy (8)
- Biology (8)
- Biomedical (14)
- Biotechnology (1)
- Buildings (1)
- Chemical Sciences (5)
- Composites (1)
- Computer Science (48)
- Critical Materials (3)
- Cybersecurity (7)
- Environment (10)
- Exascale Computing (8)
- Fusion (2)
- Grid (3)
- High-Performance Computing (15)
- Machine Learning (6)
- Materials Science (20)
- Microscopy (6)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (5)
- Neutron Science (63)
- Nuclear Energy (4)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (12)
- Polymers (2)
- Quantum Computing (9)
- Quantum Science (17)
- Security (4)
- Simulation (2)
- Summit (20)
- Transportation (5)
Media Contacts

Researchers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Oak Ridge National Laboratory successfully created amorphous ice, similar to ice in interstellar space and on icy worlds in our solar system. They documented that its disordered atomic behavior is unlike any ice on Earth.

The Department of Energy’s Office of Science has selected five Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists for Early Career Research Program awards.

The U.S. Department of Energy’s Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment, or INCITE, program is seeking proposals for high-impact, computationally intensive research campaigns in a broad array of science, engineering and computer science domains.

Scientists have found new, unexpected behaviors when SARS-CoV-2 – the virus that causes COVID-19 – encounters drugs known as inhibitors, which bind to certain components of the virus and block its ability to reproduce.
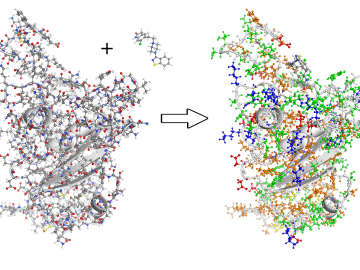
To better understand the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have harnessed the power of supercomputers to accurately model the spike protein that binds the novel coronavirus to a human cell receptor.

Six scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory were named Battelle Distinguished Inventors, in recognition of obtaining 14 or more patents during their careers at the lab.

The annual Director's Awards recognized four individuals and teams including awards for leadership in quantum simulation development and application on high-performance computing platforms, and revolutionary advancements in the area of microbial
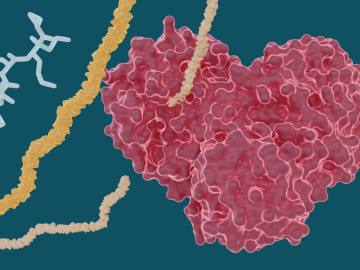
Experiments led by researchers at ORNL have determined that several hepatitis C drugs can inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, a crucial protein enzyme that enables the novel coronavirus to reproduce.

To better understand how the novel coronavirus behaves and how it can be stopped, scientists have completed a three-dimensional map that reveals the location of every atom in an enzyme molecule critical to SARS-CoV-2 reproduction.

A team led by Dan Jacobson of Oak Ridge National Laboratory used the Summit supercomputer at ORNL to analyze genes from cells in the lung fluid of nine COVID-19 patients compared with 40 control patients.


