
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (20)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Energy Science (41)
- Fusion and Fission (11)
- Fusion Energy (3)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials (48)
- Materials for Computing (4)
- National Security (5)
- Neutron Science (18)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (8)
- Supercomputing (30)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (12)
- (-) Bioenergy (25)
- (-) Biomedical (17)
- (-) Chemical Sciences (35)
- (-) Critical Materials (11)
- (-) Frontier (16)
- (-) Fusion (18)
- (-) Grid (16)
- (-) Physics (26)
- (-) Space Exploration (3)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (49)
- Artificial Intelligence (35)
- Big Data (8)
- Biology (26)
- Biotechnology (10)
- Buildings (15)
- Clean Water (2)
- Composites (12)
- Computer Science (63)
- Coronavirus (17)
- Cybersecurity (17)
- Education (3)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (43)
- Environment (38)
- Exascale Computing (13)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- High-Performance Computing (32)
- Isotopes (20)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (13)
- Materials (60)
- Materials Science (56)
- Mercury (2)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (17)
- Molten Salt (3)
- Nanotechnology (29)
- National Security (18)
- Neutron Science (54)
- Nuclear Energy (28)
- Partnerships (31)
- Polymers (13)
- Quantum Computing (13)
- Quantum Science (31)
- Security (12)
- Simulation (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (22)
- Transportation (26)
Media Contacts
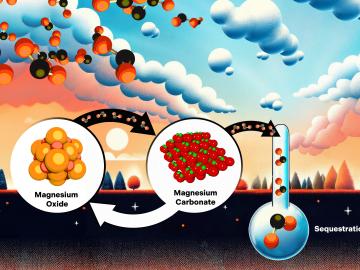
Magnesium oxide is a promising material for capturing carbon dioxide directly from the atmosphere and injecting it deep underground to limit the effects of climate change. ORNL scientists are exploring ways to overcome an obstacle to making the technology economical.
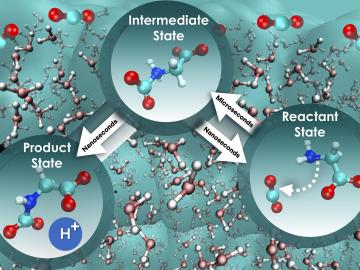
Recent research by ORNL scientists focused on the foundational steps of carbon dioxide sequestration using aqueous glycine, an amino acid known for its absorbent qualities.

Four scientists affiliated with ORNL were named Battelle Distinguished Inventors during the lab’s annual Innovation Awards on Dec. 1 in recognition of being granted 14 or more United States patents.

Caldera Holding, the owner and developer of Missouri’s Pea Ridge iron mine, has entered a nonexclusive research and development licensing agreement with ORNL to apply a membrane solvent extraction technique, or MSX, developed by ORNL researchers to mined ores.

Guided by machine learning, chemists at ORNL designed a record-setting carbonaceous supercapacitor material that stores four times more energy than the best commercial material.

Researchers at ORNL have been leading a project to understand how a high-altitude electromagnetic pulse, or EMP, could threaten power plants.

Scientists at ORNL used their expertise in quantum biology, artificial intelligence and bioengineering to improve how CRISPR Cas9 genome editing tools work on organisms like microbes that can be modified to produce renewable fuels and chemicals.

In a finding that helps elucidate how molten salts in advanced nuclear reactors might behave, scientists have shown how electrons interacting with the ions of the molten salt can form three states with different properties. Understanding these states can help predict the impact of radiation on the performance of salt-fueled reactors.

ORNL has been selected to lead an Energy Earthshot Research Center, or EERC, focused on developing chemical processes that use sustainable methods instead of burning fossil fuels to radically reduce industrial greenhouse gas emissions to stem climate change and limit the crisis of a rapidly warming planet.

Using light instead of heat, researchers at ORNL have found a new way to release carbon dioxide, or CO2, from a solvent used in direct air capture, or DAC, to trap this greenhouse gas. The novel approach paves the way for economically viable separation of CO2 from the atmosphere.


