
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (4)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (4)
- Energy Science (10)
- Fusion and Fission (2)
- Fusion Energy (6)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (11)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- Mathematics (1)
- Neutron Science (3)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (6)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Supercomputing (6)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Clean Water (14)
- (-) Fusion (9)
- (-) Machine Learning (14)
- (-) Mathematics (3)
- (-) Microscopy (11)
- (-) Molten Salt (5)
- (-) Quantum Science (12)
- (-) Space Exploration (10)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (34)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (16)
- Big Data (17)
- Bioenergy (17)
- Biology (21)
- Biomedical (11)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (21)
- Chemical Sciences (13)
- Composites (11)
- Computer Science (42)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Critical Materials (12)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (32)
- Environment (48)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Grid (22)
- High-Performance Computing (12)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (5)
- ITER (3)
- Materials (36)
- Materials Science (34)
- Mercury (3)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (27)
- Nuclear Energy (19)
- Partnerships (2)
- Physics (4)
- Polymers (10)
- Quantum Computing (5)
- Security (1)
- Simulation (9)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Transportation (36)
Media Contacts
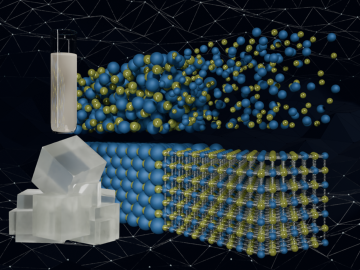
Scientists have developed a new machine learning approach that accurately predicted critical and difficult-to-compute properties of molten salts, materials with diverse nuclear energy applications.

Working in collaboration with researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory, D-Wave Quantum Inc., a quantum computing systems, software and services provider, has shown its annealing quantum computing prototype has the potential to operate faster than the leading supercomputing systems.

Researchers at Stanford University, the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, or ECMWF, and ORNL used the lab’s Summit supercomputer to better understand atmospheric gravity waves, which influence significant weather patterns that are difficult to forecast.

Researchers have identified a molecule essential for the microbial conversion of inorganic mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury, moving closer to blocking the dangerous pollutant before it forms.

A digital construction platform in development at Oak Ridge National Laboratory is boosting the retrofitting of building envelopes and giving builders the tools to automate the process from design to installation with the assistance of a cable-driven robotic crane.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have developed a method leveraging artificial intelligence to accelerate the identification of environmentally friendly solvents for industrial carbon capture, biomass processing, rechargeable batteries and other applications.

Groundwater withdrawals are expected to peak in about one-third of the world’s basins by 2050, potentially triggering significant trade and agriculture shifts, a new analysis finds.

To capitalize on AI and researcher strengths, scientists developed a human-AI collaboration recommender system for improved experimentation performance.

ORNL climate modeling expertise contributed to a project that assessed global emissions of ammonia from croplands now and in a warmer future, while also identifying solutions tuned to local growing conditions.

A study led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers identifies a new potential application in quantum computing that could be part of the next computational revolution.


