
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (26)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (4)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Science (55)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fusion and Fission (1)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotopes (3)
- Materials (25)
- Materials for Computing (5)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (8)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (6)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (17)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Bioenergy (17)
- (-) Biomedical (11)
- (-) Composites (11)
- (-) Energy Storage (32)
- (-) Environment (48)
- (-) Frontier (1)
- (-) Grid (22)
- (-) Molten Salt (5)
- (-) Nanotechnology (12)
- (-) Polymers (10)
- (-) Quantum Science (11)
- (-) Space Exploration (10)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (34)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (16)
- Big Data (17)
- Biology (21)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (21)
- Chemical Sciences (13)
- Clean Water (14)
- Computer Science (42)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Critical Materials (12)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Emergency (1)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Fusion (9)
- High-Performance Computing (12)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (5)
- ITER (3)
- Machine Learning (14)
- Materials (36)
- Materials Science (34)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (3)
- Microscopy (11)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (27)
- Nuclear Energy (19)
- Partnerships (2)
- Physics (4)
- Quantum Computing (5)
- Security (1)
- Simulation (9)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Transportation (36)
Media Contacts

By automating the production of neptunium oxide-aluminum pellets, Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have eliminated a key bottleneck when producing plutonium-238 used by NASA to fuel deep space exploration.

Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Hypres, a digital superconductor company, have tested a novel cryogenic, or low-temperature, memory cell circuit design that may boost memory storage while using less energy in future exascale and quantum computing applications.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists studying fuel cells as a potential alternative to internal combustion engines used sophisticated electron microscopy to investigate the benefits of replacing high-cost platinum with a lower cost, carbon-nitrogen-manganese-based catalyst.
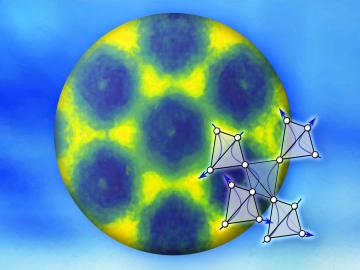
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to investigate bizarre magnetic behavior, believed to be a possible quantum spin liquid rarely found in a three-dimensional material. QSLs are exotic states of matter where magnetism continues to fluctuate at low temperatures instead of “freezing” into aligned north and south poles as with traditional magnets.
![2018-P07635 BL-6 user - Univ of Guelph-6004R_sm[2].jpg 2018-P07635 BL-6 user - Univ of Guelph-6004R_sm[2].jpg](/sites/default/files/styles/list_page_thumbnail/public/2018-P07635%20BL-6%20user%20-%20Univ%20of%20Guelph-6004R_sm%5B2%5D.jpg?itok=hUSyvkP0)
A team of scientists, led by University of Guelph professor John Dutcher, are using neutrons at ORNL’s Spallation Neutron Source to unlock the secrets of natural nanoparticles that could be used to improve medicines.

Scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory performed a corrosion test in a neutron radiation field to support the continued development of molten salt reactors.
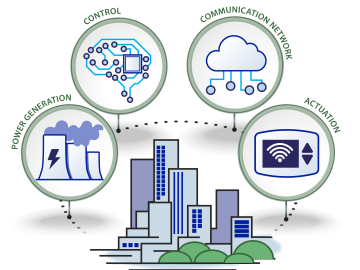
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have devised a method to control the heating and cooling systems of a large network of buildings for power grid stability—all while ensuring the comfort of occupants.

Experts focused on the future of nuclear technology will gather at Oak Ridge National Laboratory for the fourth annual Molten Salt Reactor Workshop on October 3–4.

An Oak Ridge National Laboratory-led team used a scanning transmission electron microscope to selectively position single atoms below a crystal’s surface for the first time.

Biologists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center have confirmed that microorganisms called methanogens can transform mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury with varying efficiency across species.


