
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (11)
- Biology and Environment (6)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (6)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Science (43)
- Fusion and Fission (3)
- Fusion Energy (6)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (14)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (2)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (9)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (34)
- (-) Critical Materials (12)
- (-) Fusion (9)
- (-) Grid (22)
- (-) Machine Learning (14)
- (-) Mercury (3)
- (-) Partnerships (2)
- (-) Quantum Science (11)
- (-) Security (1)
- (-) Simulation (9)
- (-) Space Exploration (10)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (16)
- Big Data (17)
- Bioenergy (17)
- Biology (21)
- Biomedical (11)
- Biotechnology (4)
- Buildings (21)
- Chemical Sciences (13)
- Clean Water (14)
- Composites (11)
- Computer Science (42)
- Coronavirus (11)
- Cybersecurity (3)
- Emergency (1)
- Energy Storage (32)
- Environment (48)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (1)
- High-Performance Computing (12)
- Hydropower (6)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (5)
- ITER (3)
- Materials (36)
- Materials Science (34)
- Mathematics (3)
- Microscopy (11)
- Molten Salt (5)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (3)
- Neutron Science (27)
- Nuclear Energy (19)
- Physics (4)
- Polymers (10)
- Quantum Computing (5)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (8)
- Transportation (36)
Media Contacts

Scientists have tested a novel heat-shielding graphite foam, originally created at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, at Germany’s Wendelstein 7-X stellarator with promising results for use in plasma-facing components of fusion reactors.

By automating the production of neptunium oxide-aluminum pellets, Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have eliminated a key bottleneck when producing plutonium-238 used by NASA to fuel deep space exploration.
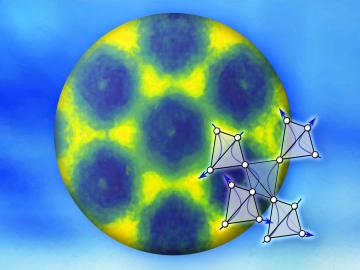
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to investigate bizarre magnetic behavior, believed to be a possible quantum spin liquid rarely found in a three-dimensional material. QSLs are exotic states of matter where magnetism continues to fluctuate at low temperatures instead of “freezing” into aligned north and south poles as with traditional magnets.

Thought leaders from across the maritime community came together at Oak Ridge National Laboratory to explore the emerging new energy landscape for the maritime transportation system during the Ninth Annual Maritime Risk Symposium.
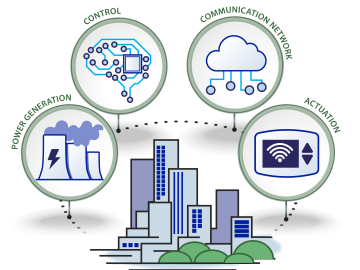
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have devised a method to control the heating and cooling systems of a large network of buildings for power grid stability—all while ensuring the comfort of occupants.

Scientists from the Critical Materials Institute used the Titan supercomputer and Eos computing cluster at ORNL to analyze designer molecules that could increase the yield of rare earth elements found in bastnaesite, an important mineral

Biologists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center have confirmed that microorganisms called methanogens can transform mercury into the neurotoxin methylmercury with varying efficiency across species.

The construction industry may soon benefit from 3D printed molds to make concrete facades, promising lower cost and production time. Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory are evaluating the performance of 3D printed molds used to precast concrete facades in a 42-story buildin...

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists have improved a mixture of materials used to 3D print permanent magnets with increased density, which could yield longer lasting, better performing magnets for electric motors, sensors and vehicle applications. Building on previous research, ...
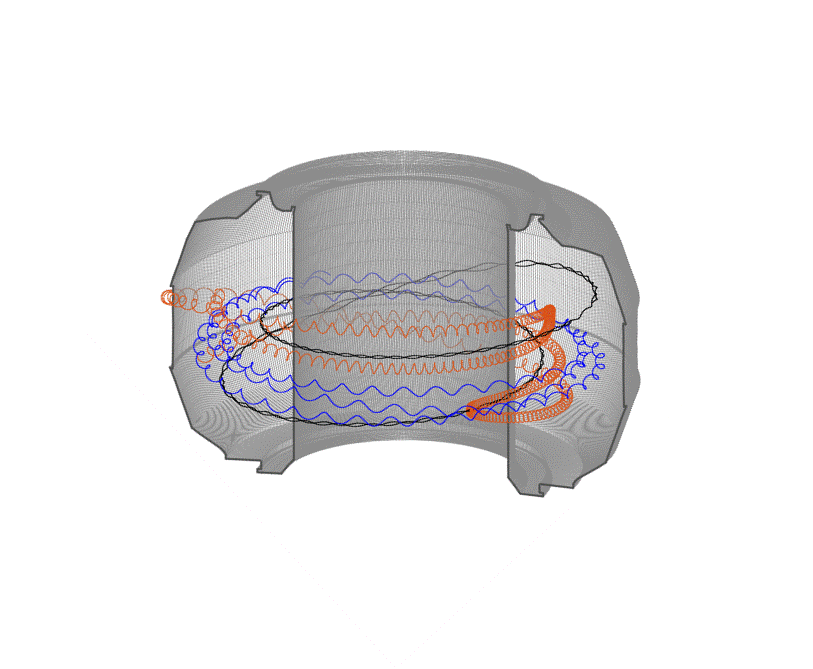
Fusion scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory are studying the behavior of high-energy electrons when the plasma that generates nuclear fusion energy suddenly cools during a magnetic disruption. Fusion energy is created when hydrogen isotopes are heated to millions of degrees...


