
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Neutron Science (30)
- (-) Supercomputing (70)
- Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Biology and Environment (26)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (5)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Science (41)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (4)
- Fusion Energy (3)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials (88)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (18)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- National Security (9)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (3)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) Big Data (23)
- (-) Materials Science (33)
- (-) Polymers (3)
- (-) Summit (43)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (11)
- Advanced Reactors (2)
- Artificial Intelligence (40)
- Bioenergy (14)
- Biology (16)
- Biomedical (28)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (7)
- Chemical Sciences (7)
- Clean Water (2)
- Composites (1)
- Computer Science (100)
- Coronavirus (19)
- Critical Materials (3)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Energy Storage (14)
- Environment (29)
- Exascale Computing (26)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (33)
- Fusion (2)
- Grid (5)
- High-Performance Computing (44)
- Hydropower (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Machine Learning (17)
- Materials (28)
- Mathematics (2)
- Microscopy (8)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (19)
- National Security (8)
- Neutron Science (122)
- Nuclear Energy (7)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (17)
- Quantum Computing (20)
- Quantum Science (30)
- Security (7)
- Simulation (16)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (5)
- Transportation (10)
Media Contacts
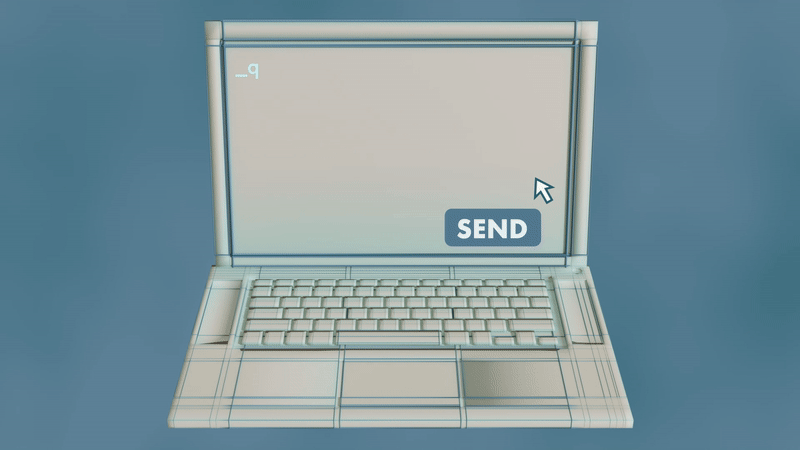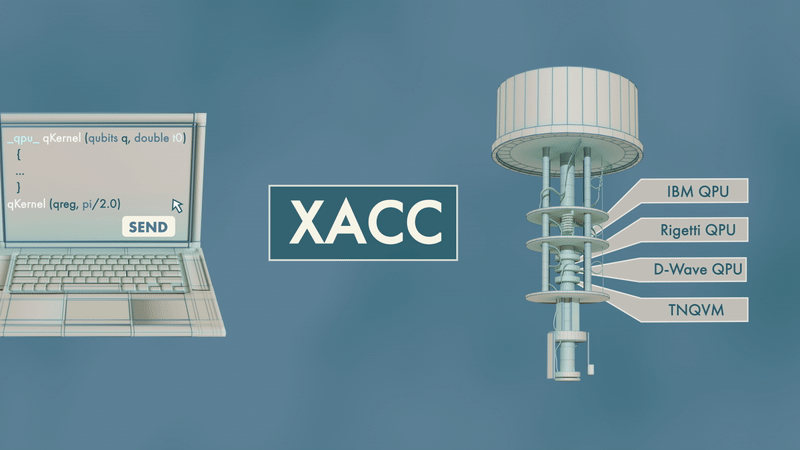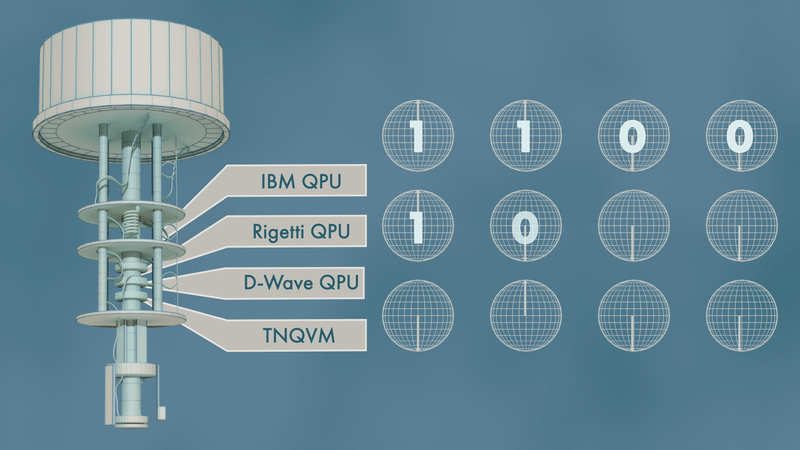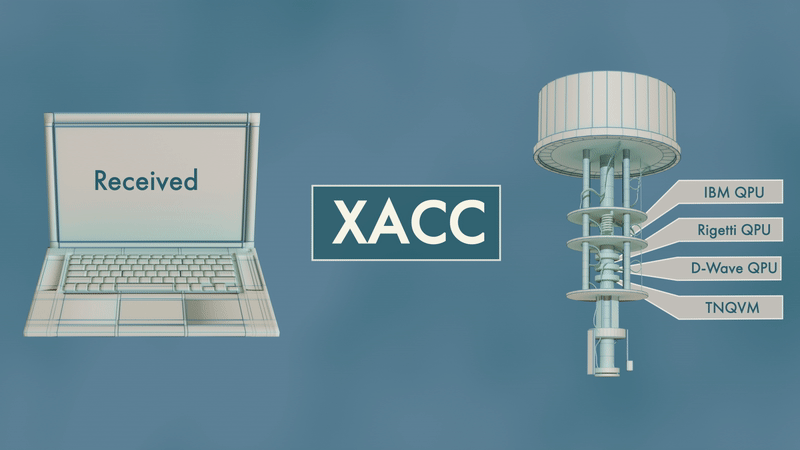
In the early 2000s, high-performance computing experts repurposed GPUs — common video game console components used to speed up image rendering and other time-consuming tasks

In the race to identify solutions to the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are joining the fight by applying expertise in computational science, advanced manufacturing, data science and neutron science.

Biological membranes, such as the “walls” of most types of living cells, primarily consist of a double layer of lipids, or “lipid bilayer,” that forms the structure, and a variety of embedded and attached proteins with highly specialized functions, including proteins that rapidly and selectively transport ions and molecules in and out of the cell.

We have a data problem. Humanity is now generating more data than it can handle; more sensors, smartphones, and devices of all types are coming online every day and contributing to the ever-growing global dataset.

As the second-leading cause of death in the United States, cancer is a public health crisis that afflicts nearly one in two people during their lifetime.

A novel approach developed by scientists at ORNL can scan massive datasets of large-scale satellite images to more accurately map infrastructure – such as buildings and roads – in hours versus days.

The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.

Scientists at have experimentally demonstrated a novel cryogenic, or low temperature, memory cell circuit design based on coupled arrays of Josephson junctions, a technology that may be faster and more energy efficient than existing memory devices.

Researchers across the scientific spectrum crave data, as it is essential to understanding the natural world and, by extension, accelerating scientific progress.


