
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Biology and Environment (108)
- (-) Energy Science (86)
- (-) Neutron Science (125)
- (-) Supercomputing (107)
- Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (8)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (32)
- Fusion Energy (13)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (26)
- Materials (95)
- Materials for Computing (7)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (40)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (42)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (2)
- Quantum information Science (2)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (7)
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (48)
- (-) Clean Water (21)
- (-) Cybersecurity (15)
- (-) Environment (152)
- (-) Isotopes (3)
- (-) Neutron Science (123)
- (-) Nuclear Energy (13)
- (-) Physics (18)
- (-) Summit (48)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (84)
- Big Data (35)
- Bioenergy (70)
- Biology (85)
- Biomedical (43)
- Biotechnology (18)
- Buildings (39)
- Chemical Sciences (23)
- Composites (19)
- Computer Science (119)
- Coronavirus (35)
- Critical Materials (12)
- Energy Storage (78)
- Exascale Computing (29)
- Fossil Energy (3)
- Frontier (33)
- Fusion (3)
- Grid (42)
- High-Performance Computing (58)
- Hydropower (10)
- Machine Learning (27)
- Materials (59)
- Materials Science (59)
- Mathematics (7)
- Mercury (10)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (21)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (26)
- National Security (12)
- Partnerships (13)
- Polymers (15)
- Quantum Computing (20)
- Quantum Science (31)
- Security (11)
- Simulation (28)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (8)
- Statistics (1)
- Transportation (72)
Media Contacts

Tempering, the heating process that gives chocolate its appealing sheen and creamy texture, is a crucial part of crafting quality chocolate. But, at the molecular level, it gets a little tricky, and when done incorrectly, can render entire batches of chocolate gritty and unappetizing.
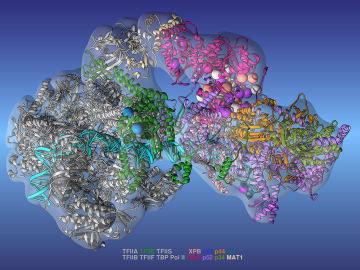
Environmental conditions, lifestyle choices, chemical exposure, and foodborne and airborne pathogens are among the external factors that can cause disease. In contrast, internal genetic factors can be responsible for the onset and progression of diseases ranging from degenerative neurological disorders to some cancers.

OAK RIDGE, Tenn., May 14, 2019—Advanced Research Systems, Inc., has licensed a technology designed to automatically refill liquid helium used in laboratory equipment for low-temperature scientific experiments, which will reduce downtime, recover more helium and increase overall efficiency.

Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and Washington State University teamed up to investigate the complex dynamics of low-water liquids that challenge nuclear waste processing at federal cleanup sites.
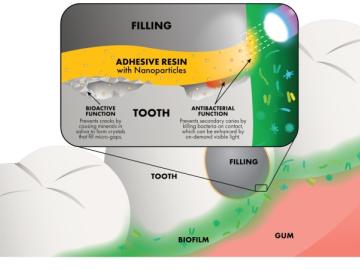
To help address the issue of dental restoration, Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers are using neutron scattering to study how nanoparticles with antibacterial properties can be added to adhesive resins, which are used by dentists to strengthen the bond between a tooth and its polymer composite filling.

Using Summit, the world’s most powerful supercomputer housed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, a team led by Argonne National Laboratory ran three of the largest cosmological simulations known to date.

In a step toward advancing small modular nuclear reactor designs, scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have run reactor simulations on ORNL supercomputer Summit with greater-than-expected computational efficiency.
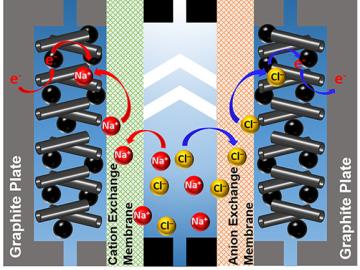
A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory used carbon nanotubes to improve a desalination process that attracts and removes ionic compounds such as salt from water using charged electrodes.

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are working to understand both the complex nature of uranium and the various oxide forms it can take during processing steps that might occur throughout the nuclear fuel cycle.

Using artificial neural networks designed to emulate the inner workings of the human brain, deep-learning algorithms deftly peruse and analyze large quantities of data. Applying this technique to science problems can help unearth historically elusive solutions.


