
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Computational Engineering (1)
- (-) Neutron Science (53)
- Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Biology and Environment (37)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computer Science (10)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Science (137)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (13)
- Fusion Energy (8)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials (124)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (19)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- National Security (27)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (19)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (9)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (73)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (1)
- (-) Coronavirus (10)
- (-) Machine Learning (4)
- (-) Materials Science (23)
- (-) Physics (9)
- (-) Quantum Science (7)
- (-) Transportation (5)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Big Data (3)
- Bioenergy (7)
- Biology (7)
- Biomedical (15)
- Biotechnology (1)
- Chemical Sciences (3)
- Clean Water (3)
- Composites (1)
- Computer Science (16)
- Cybersecurity (1)
- Energy Storage (6)
- Environment (9)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (1)
- High-Performance Computing (3)
- Hydropower (1)
- Materials (14)
- Mathematics (2)
- Microscopy (3)
- Nanotechnology (10)
- National Security (2)
- Neutron Science (120)
- Nuclear Energy (3)
- Polymers (1)
- Quantum Computing (1)
- Security (2)
- Space Exploration (3)
- Summit (7)
Media Contacts

In the race to identify solutions to the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are joining the fight by applying expertise in computational science, advanced manufacturing, data science and neutron science.

An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.

ORNL computer scientist Catherine Schuman returned to her alma mater, Harriman High School, to lead Hour of Code activities and talk to students about her job as a researcher.

Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have new experimental evidence and a predictive theory that solves a long-standing materials science mystery: why certain crystalline materials shrink when heated.

A study led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory explored the interface between the Department of Veterans Affairs’ healthcare data system and the data itself to detect the likelihood of errors and designed an auto-surveillance tool
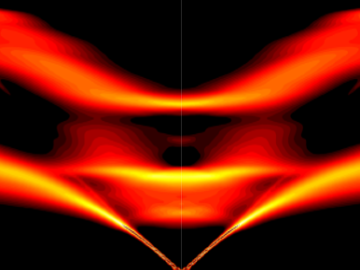
Scientists have discovered a way to alter heat transport in thermoelectric materials, a finding that may ultimately improve energy efficiency as the materials

An ORNL-led team's observation of certain crystalline ice phases challenges accepted theories about super-cooled water and non-crystalline ice. Their findings, reported in the journal Nature, will also lead to better understanding of ice and its various phases found on other planets, moons and elsewhere in space.
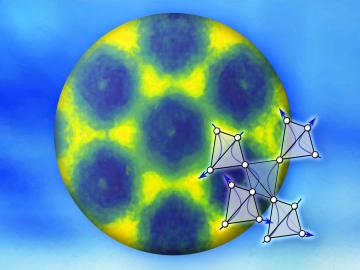
Researchers used neutron scattering at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s Spallation Neutron Source to investigate bizarre magnetic behavior, believed to be a possible quantum spin liquid rarely found in a three-dimensional material. QSLs are exotic states of matter where magnetism continues to fluctuate at low temperatures instead of “freezing” into aligned north and south poles as with traditional magnets.

A team of scientists has for the first time measured the elusive weak interaction between protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. They had chosen the simplest nucleus consisting of one neutron and one proton for the study.



