
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Energy Science (56)
- (-) Neutron Science (41)
- (-) Nuclear Science and Technology (15)
- Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (38)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (16)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (27)
- Fusion Energy (15)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (8)
- Materials (97)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (18)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (26)
- Quantum information Science (6)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (122)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) Biomedical (22)
- (-) Computer Science (37)
- (-) Exascale Computing (2)
- (-) Fusion (10)
- (-) Materials Science (51)
- (-) Security (8)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (86)
- Advanced Reactors (15)
- Artificial Intelligence (14)
- Big Data (7)
- Bioenergy (31)
- Biology (18)
- Biotechnology (5)
- Buildings (38)
- Chemical Sciences (17)
- Clean Water (10)
- Composites (18)
- Coronavirus (23)
- Critical Materials (9)
- Cybersecurity (10)
- Energy Storage (74)
- Environment (59)
- Fossil Energy (3)
- Frontier (3)
- Grid (39)
- High-Performance Computing (8)
- Hydropower (3)
- Isotopes (6)
- Machine Learning (10)
- Materials (46)
- Mathematics (3)
- Mercury (3)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (10)
- Molten Salt (5)
- Nanotechnology (17)
- National Security (7)
- Neutron Science (123)
- Nuclear Energy (42)
- Partnerships (12)
- Physics (11)
- Polymers (12)
- Quantum Computing (1)
- Quantum Science (8)
- Simulation (4)
- Space Exploration (10)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (9)
- Transportation (68)
Media Contacts

Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have new experimental evidence and a predictive theory that solves a long-standing materials science mystery: why certain crystalline materials shrink when heated.

Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have received five 2019 R&D 100 Awards, increasing the lab’s total to 221 since the award’s inception in 1963.

ORNL and The University of Toledo have entered into a memorandum of understanding for collaborative research.

Quanex Building Products has signed a non-exclusive agreement to license a method to produce insulating material from ORNL. The low-cost material can be used as an additive to increase thermal insulation performance and improve energy efficiency when applied to a variety of building products.

A team including Oak Ridge National Laboratory and University of Tennessee researchers demonstrated a novel 3D printing approach called Z-pinning that can increase the material’s strength and toughness by more than three and a half times compared to conventional additive manufacturing processes.

IDEMIA Identity & Security USA has licensed an advanced optical array developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The portable technology can be used to help identify individuals in challenging outdoor conditions.
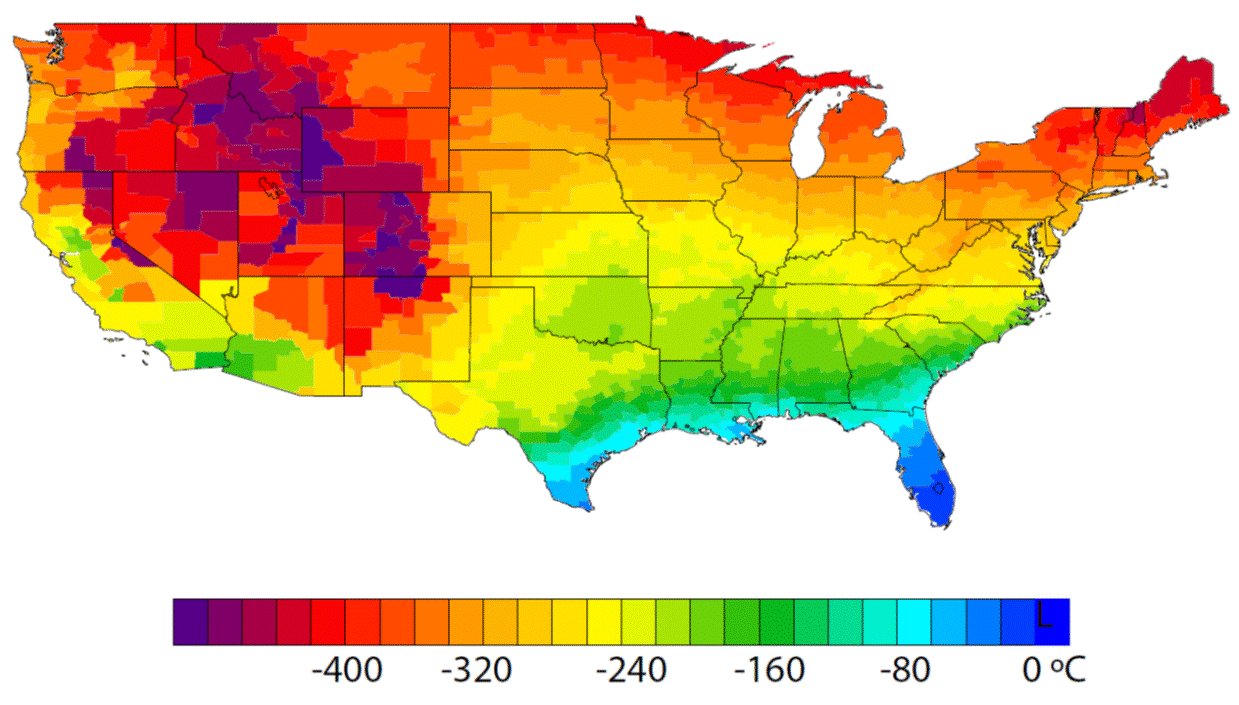
A detailed study by Oak Ridge National Laboratory estimated how much more—or less—energy United States residents might consume by 2050 relative to predicted shifts in seasonal weather patterns

A new method developed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory improves the energy efficiency of a desalination process known as solar-thermal evaporation.
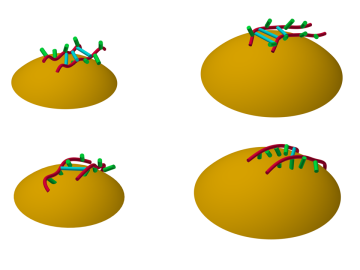
A team of researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated that designed synthetic polymers can serve as a high-performance binding material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries.
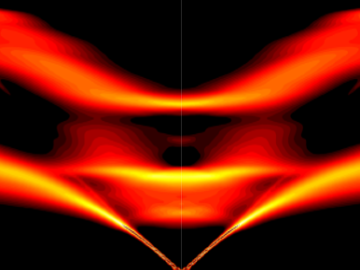
Scientists have discovered a way to alter heat transport in thermoelectric materials, a finding that may ultimately improve energy efficiency as the materials


