
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Energy Science (26)
- (-) Fusion Energy (1)
- (-) Neutron Science (123)
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (30)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (1)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Fusion and Fission (2)
- Materials (70)
- Materials for Computing (12)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (6)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (5)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (79)
News Topics
- (-) Mathematics (3)
- (-) Mercury (3)
- (-) Nanotechnology (17)
- (-) Neutron Science (121)
- (-) Quantum Computing (1)
- (-) Summit (10)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (84)
- Advanced Reactors (13)
- Artificial Intelligence (14)
- Big Data (7)
- Bioenergy (31)
- Biology (18)
- Biomedical (20)
- Biotechnology (5)
- Buildings (38)
- Chemical Sciences (17)
- Clean Water (10)
- Composites (18)
- Computer Science (37)
- Coronavirus (22)
- Critical Materials (9)
- Cybersecurity (9)
- Energy Storage (74)
- Environment (59)
- Exascale Computing (2)
- Fossil Energy (3)
- Frontier (4)
- Fusion (17)
- Grid (39)
- High-Performance Computing (8)
- Hydropower (3)
- Isotopes (1)
- Machine Learning (10)
- Materials (47)
- Materials Science (50)
- Microelectronics (1)
- Microscopy (10)
- Molten Salt (1)
- National Security (7)
- Nuclear Energy (19)
- Partnerships (12)
- Physics (10)
- Polymers (12)
- Quantum Science (8)
- Security (8)
- Simulation (4)
- Space Exploration (6)
- Statistics (1)
- Transportation (68)
Media Contacts

In the race to identify solutions to the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory are joining the fight by applying expertise in computational science, advanced manufacturing, data science and neutron science.
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers working on neutron imaging capabilities for nuclear materials have developed a process for seeing the inside of uranium particles – without cutting them open.

A versatile class of flexible, protein-like polymers could significantly advance future drug delivery methods. But first, scientists have to develop a reliable process for tailoring these polymers into shapes that can effectively transport medicines throughout the human body.

Biological membranes, such as the “walls” of most types of living cells, primarily consist of a double layer of lipids, or “lipid bilayer,” that forms the structure, and a variety of embedded and attached proteins with highly specialized functions, including proteins that rapidly and selectively transport ions and molecules in and out of the cell.

The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.
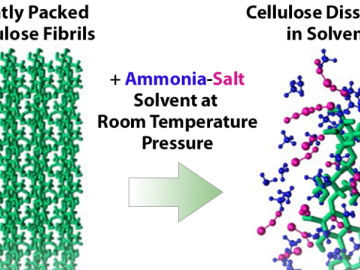
Researchers have developed a new process that could make it much cheaper to produce biofuels such as ethanol from plant waste and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.

Illustration of the optimized zeolite catalyst, or NbAlS-1, which enables a highly efficient chemical reaction to create butene, a renewable source of energy, without expending high amounts of energy for the conversion. Credit: Jill Hemman, Oak Ridge National Laboratory/U.S. Dept. of Energy
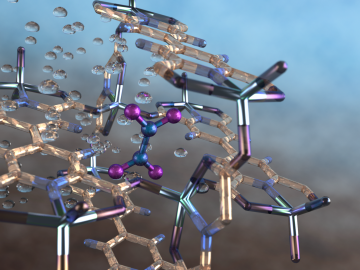
An international team of scientists, led by the University of Manchester, has developed a metal-organic framework, or MOF, material



