
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Biology and Environment (90)
- (-) Materials (104)
- Advanced Manufacturing (4)
- Biological Systems (2)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (2)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Energy Science (100)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (10)
- Fusion Energy (7)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials for Computing (13)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (17)
- Neutron Science (123)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (17)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (55)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (4)
- (-) Bioenergy (52)
- (-) Grid (8)
- (-) Nanotechnology (42)
- (-) Neutron Science (36)
- (-) Physics (29)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (27)
- Artificial Intelligence (15)
- Big Data (11)
- Biology (74)
- Biomedical (20)
- Biotechnology (14)
- Buildings (5)
- Chemical Sciences (36)
- Clean Water (14)
- Composites (11)
- Computer Science (34)
- Coronavirus (14)
- Critical Materials (13)
- Cybersecurity (5)
- Energy Storage (37)
- Environment (102)
- Exascale Computing (6)
- Frontier (6)
- Fusion (8)
- High-Performance Computing (24)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (1)
- Isotopes (13)
- ITER (1)
- Machine Learning (12)
- Materials (78)
- Materials Science (82)
- Mathematics (4)
- Mercury (7)
- Microscopy (34)
- Molten Salt (3)
- National Security (5)
- Nuclear Energy (16)
- Partnerships (13)
- Polymers (18)
- Quantum Computing (3)
- Quantum Science (11)
- Security (3)
- Simulation (16)
- Space Exploration (2)
- Summit (11)
- Transportation (15)
Media Contacts

Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists studied hot springs on different continents and found similarities in how some microbes adapted despite their geographic diversity.

Speakers, scientific workshops, speed networking, a student poster showcase and more energized the Annual User Meeting of the Department of Energy’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, or CNMS, Aug. 7-10, near Market Square in downtown Knoxville, Tennessee.

Madhavi Martin brings a physicist’s tools and perspective to biological and environmental research at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, supporting advances in bioenergy, soil carbon storage and environmental monitoring, and even helping solve a murder mystery.
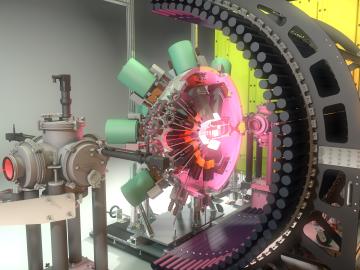
Timothy Gray of ORNL led a study that may have revealed an unexpected change in the shape of an atomic nucleus. The surprise finding could affect our understanding of what holds nuclei together, how protons and neutrons interact and how elements form.

Wildfires are an ancient force shaping the environment, but they have grown in frequency, range and intensity in response to a changing climate. At ORNL, scientists are working on several fronts to better understand and predict these events and what they mean for the carbon cycle and biodiversity.

Wildfires have shaped the environment for millennia, but they are increasing in frequency, range and intensity in response to a hotter climate. The phenomenon is being incorporated into high-resolution simulations of the Earth’s climate by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, with a mission to better understand and predict environmental change.

Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory were the first to use neutron reflectometry to peer inside a working solid-state battery and monitor its electrochemistry.

Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers recently demonstrated use of a laser-based analytical method to accelerate understanding of critical plant and soil properties that affect bioenergy plant growth and soil carbon storage.

An advance in a topological insulator material — whose interior behaves like an electrical insulator but whose surface behaves like a conductor — could revolutionize the fields of next-generation electronics and quantum computing, according to scientists at ORNL.

In a discovery aimed at accelerating the development of process-advantaged crops for jet biofuels, scientists at ORNL developed a capability to insert multiple genes into plants in a single step.


