
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biology and Environment (97)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (6)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Science (153)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (10)
- Fusion Energy (7)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (48)
- Materials for Computing (9)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (15)
- Neutron Science (22)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (11)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (9)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (58)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (40)
- (-) Clean Water (33)
- (-) Environment (218)
- (-) Grid (74)
- (-) Mathematics (12)
- (-) Microelectronics (4)
- (-) Quantum Science (93)
- (-) Transportation (103)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (146)
- Artificial Intelligence (131)
- Big Data (79)
- Bioenergy (112)
- Biology (128)
- Biomedical (73)
- Biotechnology (39)
- Buildings (74)
- Chemical Sciences (86)
- Composites (35)
- Computer Science (226)
- Coronavirus (48)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Education (5)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (114)
- Exascale Computing (67)
- Fossil Energy (8)
- Frontier (64)
- Fusion (66)
- High-Performance Computing (130)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (62)
- ITER (9)
- Machine Learning (68)
- Materials (157)
- Materials Science (158)
- Mercury (12)
- Microscopy (56)
- Molten Salt (10)
- Nanotechnology (64)
- National Security (86)
- Neutron Science (171)
- Nuclear Energy (122)
- Partnerships (68)
- Physics (69)
- Polymers (35)
- Quantum Computing (53)
- Security (31)
- Simulation (65)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (26)
- Statistics (4)
- Summit (71)
Media Contacts

Each year, approximately 6 billion gallons of fuel are wasted as vehicles wait at stop lights or sit in dense traffic with engines idling, according to US Department of Energy estimates.
A team of scientists led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory found that while all regions of the country can expect an earlier start to the growing season as temperatures rise, the trend is likely to become more variable year-over-year in hotter regions.
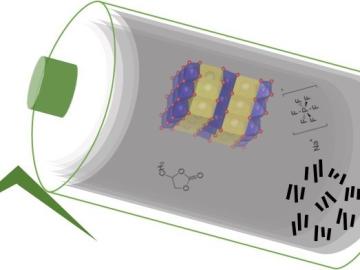
Researchers at ORNL demonstrated that sodium-ion batteries can serve as a low-cost, high performance substitute for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries commonly used in robotics, power tools, and grid-scale energy storage.

A novel approach developed by scientists at ORNL can scan massive datasets of large-scale satellite images to more accurately map infrastructure – such as buildings and roads – in hours versus days.

A team from the ORNL has conducted a series of experiments to gain a better understanding of quantum mechanics and pursue advances in quantum networking and quantum computing, which could lead to practical applications in cybersecurity and other areas.

Nuclear scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have established a Nuclear Quality Assurance-1 program for a software product designed to simulate today’s commercial nuclear reactors – removing a significant barrier for industry adoption of the technology.

To better determine the potential energy cost savings among connected homes, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a computer simulation to more accurately compare energy use on similar weather days.

Illustration of the optimized zeolite catalyst, or NbAlS-1, which enables a highly efficient chemical reaction to create butene, a renewable source of energy, without expending high amounts of energy for the conversion. Credit: Jill Hemman, Oak Ridge National Laboratory/U.S. Dept. of Energy

While Tsouris’ water research is diverse in scope, its fundamentals are based on basic science principles that remain largely unchanged, particularly in a mature field like chemical engineering.

As scientists study approaches to best sustain a fusion reactor, a team led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory investigated injecting shattered argon pellets into a super-hot plasma, when needed, to protect the reactor’s interior wall from high-energy runaway electrons.


