
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biological Systems (2)
- Biology and Environment (85)
- Building Technologies (1)
- Computational Biology (2)
- Computational Engineering (3)
- Computer Science (15)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Science (142)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (7)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (28)
- Materials (62)
- Materials for Computing (14)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (35)
- Neutron Science (36)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (12)
- Quantum information Science (7)
- Sensors and Controls (2)
- Supercomputing (133)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Topics
- (-) Bioenergy (112)
- (-) Biomedical (73)
- (-) Computer Science (226)
- (-) Grid (74)
- (-) High-Performance Computing (130)
- (-) Irradiation (3)
- (-) Isotopes (62)
- (-) Molten Salt (10)
- (-) Security (31)
- (-) Transportation (103)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (146)
- Advanced Reactors (40)
- Artificial Intelligence (131)
- Big Data (79)
- Biology (128)
- Biotechnology (39)
- Buildings (74)
- Chemical Sciences (86)
- Clean Water (33)
- Composites (35)
- Coronavirus (48)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Education (5)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (114)
- Environment (218)
- Exascale Computing (67)
- Fossil Energy (8)
- Frontier (64)
- Fusion (66)
- Hydropower (12)
- ITER (9)
- Machine Learning (68)
- Materials (157)
- Materials Science (158)
- Mathematics (12)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (4)
- Microscopy (56)
- Nanotechnology (64)
- National Security (86)
- Neutron Science (171)
- Nuclear Energy (122)
- Partnerships (68)
- Physics (69)
- Polymers (35)
- Quantum Computing (53)
- Quantum Science (93)
- Simulation (65)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (26)
- Statistics (4)
- Summit (71)
Media Contacts

The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.

A team from the ORNL has conducted a series of experiments to gain a better understanding of quantum mechanics and pursue advances in quantum networking and quantum computing, which could lead to practical applications in cybersecurity and other areas.

A typhoon strikes an island in the Pacific Ocean, downing power lines and cell towers. An earthquake hits a remote mountainous region, destroying structures and leaving no communication infrastructure behind.
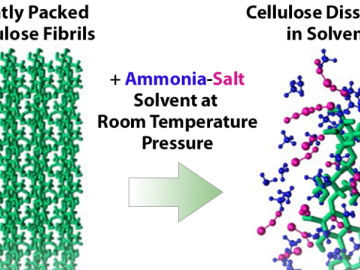
Researchers have developed a new process that could make it much cheaper to produce biofuels such as ethanol from plant waste and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.

Scientists at have experimentally demonstrated a novel cryogenic, or low temperature, memory cell circuit design based on coupled arrays of Josephson junctions, a technology that may be faster and more energy efficient than existing memory devices.

A select group gathered on the morning of Dec. 20 at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory for a symposium in honor of Liane B. Russell, the renowned ORNL mammalian geneticist who died in July.

To better determine the potential energy cost savings among connected homes, researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a computer simulation to more accurately compare energy use on similar weather days.

Researchers at ORNL have developed a quantum chemistry simulation benchmark to evaluate the performance of quantum devices and guide the development of applications for future quantum computers.

Researchers across the scientific spectrum crave data, as it is essential to understanding the natural world and, by extension, accelerating scientific progress.


