
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (2)
- Biology and Environment (75)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (4)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (3)
- Energy Science (101)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (8)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (27)
- Materials (88)
- Materials for Computing (15)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (28)
- Neutron Science (18)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (9)
- Quantum information Science (4)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (79)
News Topics
- (-) Chemical Sciences (86)
- (-) Clean Water (33)
- (-) Cybersecurity (35)
- (-) Grid (74)
- (-) Isotopes (62)
- (-) Microscopy (56)
- (-) Polymers (35)
- (-) Space Exploration (26)
- (-) Summit (71)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (146)
- Advanced Reactors (40)
- Artificial Intelligence (131)
- Big Data (79)
- Bioenergy (112)
- Biology (128)
- Biomedical (73)
- Biotechnology (39)
- Buildings (74)
- Composites (35)
- Computer Science (226)
- Coronavirus (48)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Education (5)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (114)
- Environment (218)
- Exascale Computing (67)
- Fossil Energy (8)
- Frontier (64)
- Fusion (66)
- High-Performance Computing (130)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (3)
- ITER (9)
- Machine Learning (68)
- Materials (157)
- Materials Science (158)
- Mathematics (12)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (4)
- Molten Salt (10)
- Nanotechnology (64)
- National Security (86)
- Neutron Science (171)
- Nuclear Energy (122)
- Partnerships (68)
- Physics (69)
- Quantum Computing (53)
- Quantum Science (92)
- Security (31)
- Simulation (65)
- Software (1)
- Statistics (4)
- Transportation (103)
Media Contacts
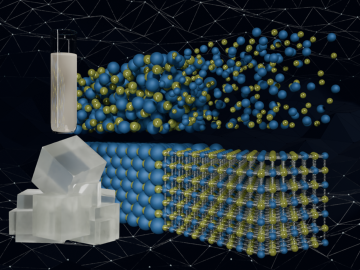
Scientists have developed a new machine learning approach that accurately predicted critical and difficult-to-compute properties of molten salts, materials with diverse nuclear energy applications.
Using the now-decommissioned Summit supercomputer, researchers at ORNL ran the largest and most accurate molecular dynamics simulations yet of the interface between water and air during a chemical reaction. The simulations have uncovered how water controls such chemical reactions by dynamically coupling with the molecules involved in the process.

ORNL’s Biological Monitoring and Abatement Program, or BMAP, is marking 40 years of helping steward the DOE’s 33,476 acres of land on which some of the nation’s most powerful science and technology missions are carried out.

Scientists at ORNL have developed a vacuum-assisted extrusion method that reduces internal porosity by up to 75% in large-scale 3D-printed polymer parts. This new technique addresses the critical issue of porosity in large-scale prints but also paves the way for stronger composites.
Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a modeling method that uses machine learning to accurately simulate electric grid behavior while protecting proprietary equipment details. The approach overcomes a key barrier to accurate grid modeling, helping utilities plan for future demand and prevent blackouts.
Robert “Bob” Hettich, an ORNL Corporate Fellow, is a pioneer in using mass spectrometry to uncover how microbes interact within complex environments and influence larger systems like plants and humans. A founder of the field of metaproteomics, he leads research that supports bioenergy, environmental resilience and health through advanced protein analysis.

A team from ORNL, joined by university students, recently traveled to the Ohio State University Research Reactor to conduct a novel experiment on nuclear thermal rocket fuel coatings — one that could help propel NASA’s astronauts to Mars faster and more efficiently.
Scientists at ORNL have developed a method that can track chemical changes in molten salt in real time — helping to pave the way for the deployment of molten salt reactors for energy production.

Researchers at Georgia State University used the Summit supercomputer to study an elaborate molecular pathway called nucleotide excision repair. Decoding NER’s sophisticated sequence of events and the role of PInC in the pathway could provide key insights into developing novel treatments and preventing conditions that lead to premature aging and certain types of cancer.

During his first visit to Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Energy Secretary Chris Wright compared the urgency of the Lab’s World War II beginnings to today’s global race to lead in artificial intelligence, calling for a “Manhattan Project 2.”


