
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (8)
- Biology and Environment (13)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computer Science (1)
- Electricity and Smart Grid (1)
- Energy Science (53)
- Functional Materials for Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (6)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (2)
- Materials (106)
- Materials Characterization (1)
- Materials for Computing (18)
- Materials Under Extremes (1)
- National Security (5)
- Neutron Science (125)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (8)
- Supercomputing (27)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- (-) Composites (35)
- (-) Materials Science (158)
- (-) Neutron Science (171)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (146)
- Advanced Reactors (40)
- Artificial Intelligence (131)
- Big Data (79)
- Bioenergy (112)
- Biology (128)
- Biomedical (73)
- Biotechnology (39)
- Buildings (74)
- Chemical Sciences (86)
- Clean Water (33)
- Computer Science (226)
- Coronavirus (48)
- Critical Materials (29)
- Cybersecurity (35)
- Education (5)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (114)
- Environment (218)
- Exascale Computing (67)
- Fossil Energy (8)
- Frontier (64)
- Fusion (66)
- Grid (74)
- High-Performance Computing (130)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (3)
- Isotopes (62)
- ITER (9)
- Machine Learning (68)
- Materials (157)
- Mathematics (12)
- Mercury (12)
- Microelectronics (4)
- Microscopy (56)
- Molten Salt (10)
- Nanotechnology (64)
- National Security (86)
- Nuclear Energy (122)
- Partnerships (68)
- Physics (69)
- Polymers (35)
- Quantum Computing (53)
- Quantum Science (93)
- Security (31)
- Simulation (65)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (26)
- Statistics (4)
- Summit (71)
- Transportation (103)
Media Contacts

An international team of researchers has discovered the hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride material are much more tightly spaced than had been predicted for decades — a feature that could possibly facilitate superconductivity at or near room temperature and pressure.

The formation of lithium dendrites is still a mystery, but materials engineers study the conditions that enable dendrites and how to stop them.

Rigoberto “Gobet” Advincula has been named Governor’s Chair of Advanced and Nanostructured Materials at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee.
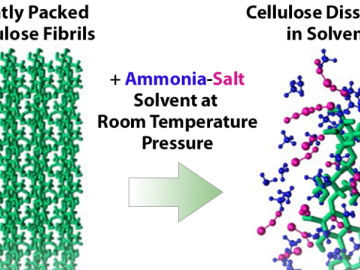
Researchers have developed a new process that could make it much cheaper to produce biofuels such as ethanol from plant waste and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.

Scientists at have experimentally demonstrated a novel cryogenic, or low temperature, memory cell circuit design based on coupled arrays of Josephson junctions, a technology that may be faster and more energy efficient than existing memory devices.

Illustration of the optimized zeolite catalyst, or NbAlS-1, which enables a highly efficient chemical reaction to create butene, a renewable source of energy, without expending high amounts of energy for the conversion. Credit: Jill Hemman, Oak Ridge National Laboratory/U.S. Dept. of Energy

Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory demonstrated that an additively manufactured polymer layer, when applied to carbon fiber reinforced plastic, or CFRP, can serve as an effective protector against aircraft lightning strikes.
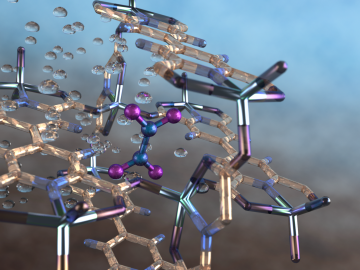
An international team of scientists, led by the University of Manchester, has developed a metal-organic framework, or MOF, material

Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have new experimental evidence and a predictive theory that solves a long-standing materials science mystery: why certain crystalline materials shrink when heated.

Two of the researchers who share the Nobel Prize in Chemistry announced Wednesday—John B. Goodenough of the University of Texas at Austin and M. Stanley Whittingham of Binghamton University in New York—have research ties to ORNL.


