Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Materials (60)
- (-) Neutron Science (32)
- Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (9)
- Clean Energy (48)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computer Science (2)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (1)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Fusion and Fission (1)
- Fusion Energy (2)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- National Security (5)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (12)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (38)
News Topics
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Artificial Intelligence (1)
- Bioenergy (6)
- Biomedical (4)
- Chemical Sciences (2)
- Climate Change (1)
- Composites (2)
- Computer Science (7)
- Coronavirus (3)
- Critical Materials (2)
- Cybersecurity (1)
- Energy Storage (5)
- Environment (5)
- Isotopes (4)
- Machine Learning (1)
- Materials (1)
- Materials Science (22)
- Microscopy (4)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (13)
- National Security (1)
- Neutron Science (22)
- Physics (7)
- Polymers (2)
- Quantum Science (6)
- Summit (4)
- Sustainable Energy (6)
- Transportation (3)
Media Contacts
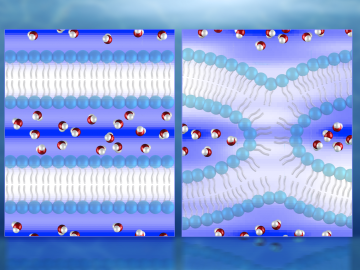

Chemists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have demonstrated a practical, energy-efficient method of capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from air. They report their findings in Nature Energy. If deployed at large scale and coupled to geo...
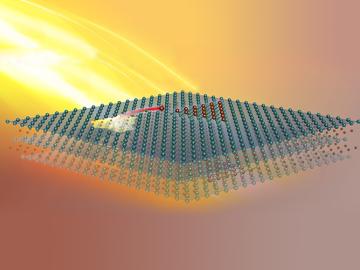
Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory induced a two-dimensional material to cannibalize itself for atomic “building blocks” from which stable structures formed. The findings, reported in Nature Communications, provide insights that ...
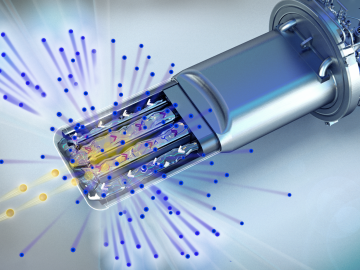

StealthCo, Inc., an Oak Ridge, Tenn.-based firm doing business as Stealth Mark, has exclusively licensed an invisible micro-taggant from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The anticounterfeiting technology features a novel materials coding system that uses an infrared marker for identification.


Led by the University of Manchester, an international team of scientists has developed a metal-organic framework material (MOF) that exhibits a selective, fully reversible and repeatable capability to remove nitrogen dioxide gas from the atmosphere in ambient conditions.

The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory is now producing actinium-227 (Ac-227) to meet projected demand for a highly effective cancer drug through a 10-year contract between the U.S. DOE Isotope Program and Bayer.


