Filter News
Area of Research
News Type
News Topics
Media Contacts
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science announced 55 projects with high potential for accelerating discovery through its Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (INCITE) program. These awards allocate the multi-petascale computing resources at Argonne and Oak Ridge National Laboratories, two of America’s most powerful supercomputers dedicated to open science.

Renewed interest in molten salt technology was evident at a recent gathering of advanced nuclear reactor experts at the US Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL). Nearly 200 attendees from national labs, industry, utilities, reactor design firms,...



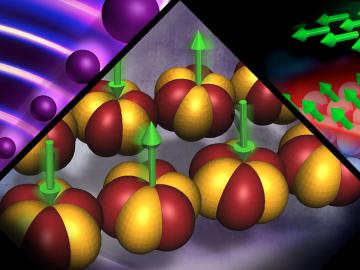
The theories recognized with this year’s Nobel Prize in Physics underpin research ongoing at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, where scientists are using neutrons as a probe to seek new materials with extraordinary properties for applications such as next-generation electronics, superconductors, and quantum computing.