Filter News
Area of Research
News Type
Date
Media Contacts

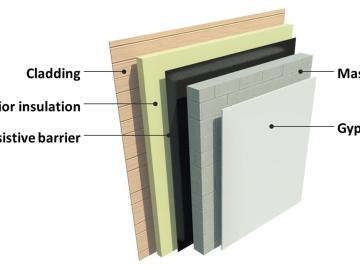
Oak Ridge National Laboratory will lead the 13th international conference on Thermal Performance of the Exterior Envelopes of Whole Buildings XIII on December 5-8 in Clearwater, Florida, an event that attracts building envelope experts from around the world to share state-of-the-art research and technology applications. One topic of interest will be a mold growth index model workshop, explaining the model’s development and application and providing examples of how MGI usage could vary depending on building materials.


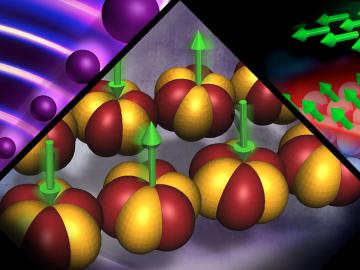
The theories recognized with this year’s Nobel Prize in Physics underpin research ongoing at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, where scientists are using neutrons as a probe to seek new materials with extraordinary properties for applications such as next-generation electronics, superconductors, and quantum computing.