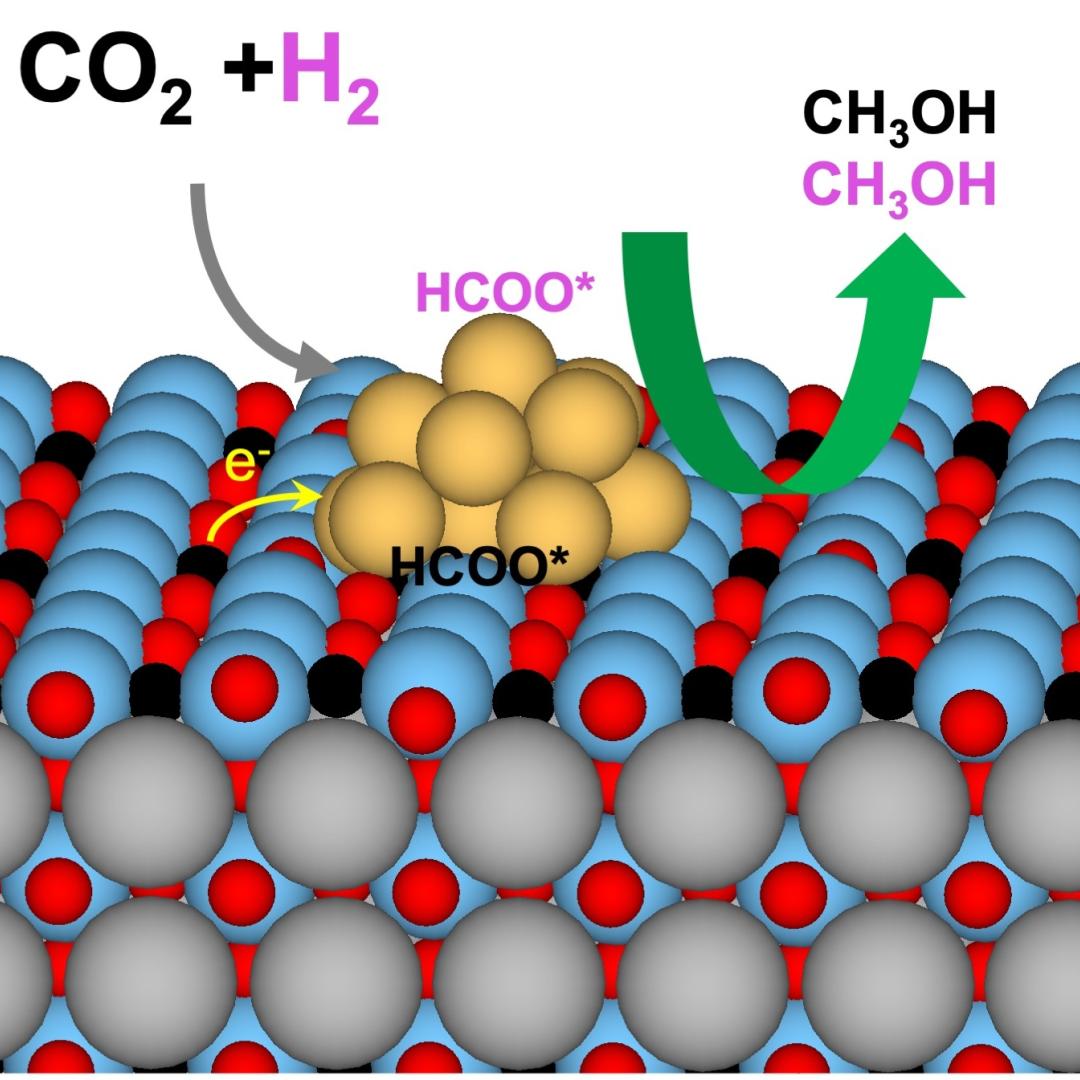
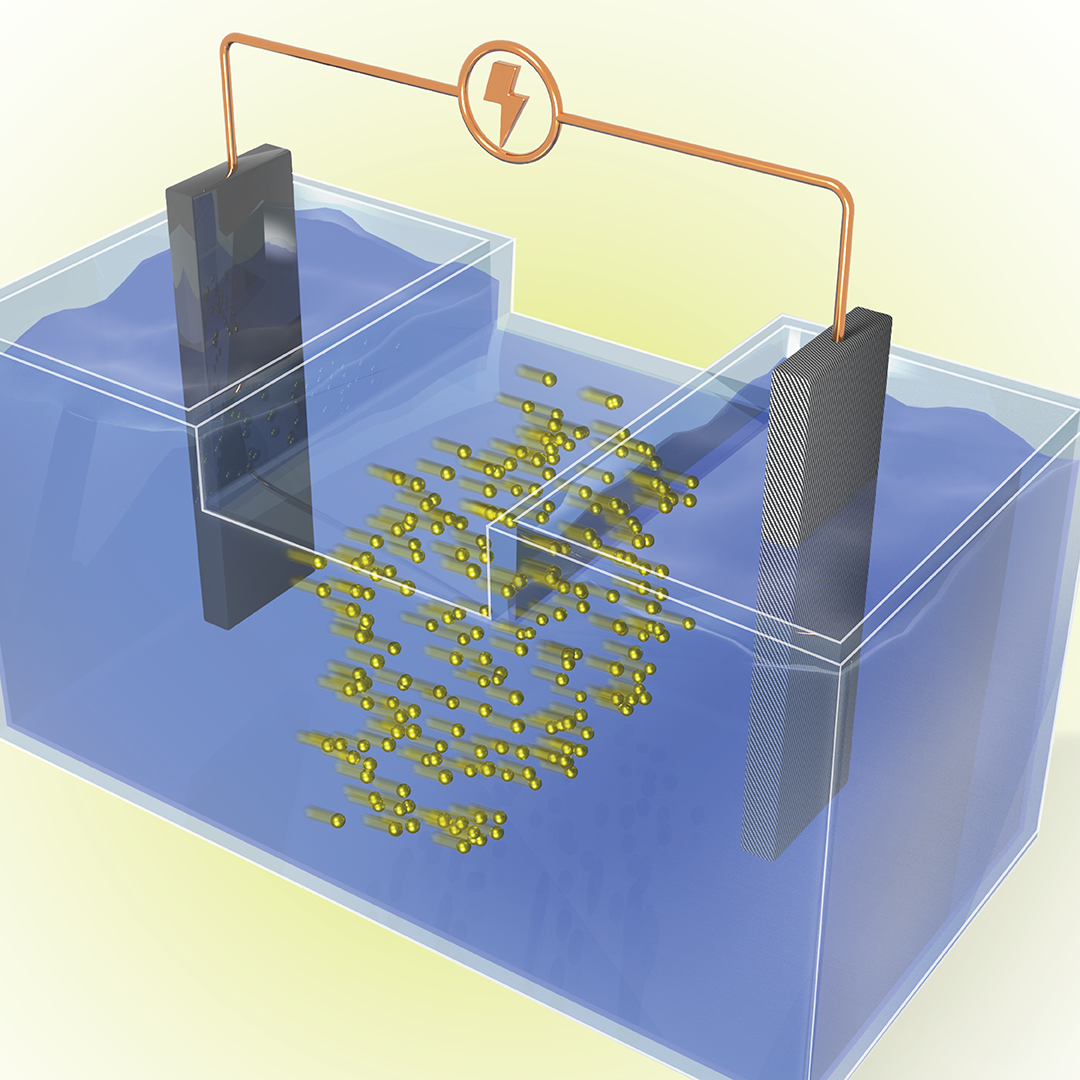
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Climate and Environmental Systems (4)
- (-) Computer Science (1)
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biological Systems (3)
- Biology and Soft Matter (3)
- Building Technologies (3)
- Chemical and Engineering Materials (2)
- Chemistry and Physics at Interfaces (5)
- Clean Energy (19)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Chemistry (4)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Earth Sciences (1)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (6)
- Fuel Cycle Science and Technology (1)
- Functional Materials for Energy (8)
- Geographic Information Science and Technology (1)
- Materials (31)
- Materials for Computing (7)
- Materials Synthesis from Atoms to Systems (8)
- Materials Under Extremes (5)
- Neutron Data Analysis and Visualization (2)
- Neutron Science (6)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (5)
- Nuclear Systems Technology (1)
- Quantum Condensed Matter (2)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (15)
- Transportation Systems (3)
News Type
Media Contacts
Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory got a surprise when they built a highly ordered lattice by layering thin films containing lanthanum, strontium, oxygen and iron. Although each layer had an intrinsically nonpolar (symmetric) distribution of electrical charges, the lattice had an asymmetric distribution of charges. The charge asymmetry creates an extra “switch” that brings new functionalities to materials when “flipped” by external stimuli such as electric fields or mechanical strain. This makes polar materials useful for devices such as sensors and actuators.

depth, population-based approach to identifying such mechanisms for adaptation, and describes a method that could be harnessed for developing more accurate predictive climate change models. For the U.S. Department of...

Thomas Wilbanks and Benjamin Preston, both of the Climate Change Science Institute (CCSI) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), are among the 309 coordinating lead authors of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC’s) Working Group II (WG II) report.

Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere may get the lion’s share of attention in climate change discussions, but the biggest repository of carbon is actually underfoot: soils store an estimated 2.5 trillion tons of carbon in the form of organic matter.

Former Energy Secretary Steven Chu mixed his Wigner Distinguished Lecture on Feb . 12 with a description of his current research at Stanford and his outlook on energy policy and climate change.