Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Biological Systems (3)
- Biology and Environment (13)
- Building Technologies (2)
- Chemistry and Physics at Interfaces (3)
- Clean Energy (61)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (2)
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (4)
- Functional Materials for Energy (3)
- Fusion and Fission (6)
- Geographic Information Science and Technology (1)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (4)
- Materials (57)
- Materials for Computing (9)
- Materials Synthesis from Atoms to Systems (2)
- Materials Under Extremes (3)
- National Security (6)
- Neutron Science (23)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (8)
- Quantum Condensed Matter (1)
- Reactor Technology (1)
- Supercomputing (29)
- Transportation Systems (2)
News Type
Date
News Topics
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (21)
- Advanced Reactors (3)
- Artificial Intelligence (4)
- Big Data (1)
- Bioenergy (7)
- Biology (6)
- Biomedical (9)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (5)
- Chemical Sciences (7)
- Climate Change (5)
- Composites (4)
- Computer Science (21)
- Coronavirus (13)
- Critical Materials (5)
- Cybersecurity (4)
- Decarbonization (2)
- Energy Storage (16)
- Environment (11)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Frontier (3)
- Fusion (6)
- Grid (4)
- High-Performance Computing (7)
- Isotopes (8)
- ITER (1)
- Machine Learning (4)
- Materials (12)
- Materials Science (26)
- Microscopy (7)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (16)
- National Security (5)
- Neutron Science (21)
- Nuclear Energy (10)
- Physics (6)
- Polymers (7)
- Quantum Computing (3)
- Quantum Science (11)
- Security (2)
- Space Exploration (2)
- Summit (12)
- Sustainable Energy (17)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (2)
- Transportation (9)
Media Contacts

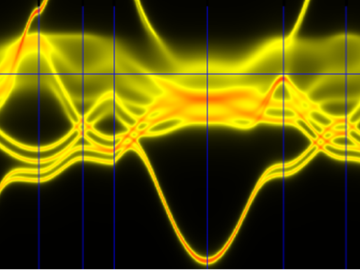




Engines, laptops and power plants generate waste heat. Thermoelectric materials, which convert temperature gradients to electricity and vice versa, can recover some of that heat and improve energy efficiency. A team of scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridg...


The Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Strangpresse LLC of Youngstown, Ohio, have signed a non-exclusive licensing agreement on a portfolio of ORNL patents related to large-scale additive manufacturing. ORNL is leading advances in the productio...

The Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Strangpresse LLC of Youngstown, Ohio, have signed a non-exclusive licensing agreement on a portfolio of ORNL patents related to large-scale additive manufacturing. ORNL is leading advances in the productio...