Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Fusion Energy (5)
- (-) Materials (71)
- Advanced Manufacturing (8)
- Biological Systems (2)
- Biology and Environment (24)
- Clean Energy (110)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (3)
- Computer Science (2)
- Data (1)
- Energy Sciences (1)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Fusion and Fission (5)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (4)
- Materials for Computing (5)
- National Security (12)
- Neutron Science (44)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (28)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (2)
- Quantum information Science (3)
- Sensors and Controls (1)
- Supercomputing (55)
- Transportation Systems (1)
News Topics
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (4)
- Advanced Reactors (4)
- Artificial Intelligence (2)
- Big Data (2)
- Bioenergy (3)
- Biomedical (1)
- Chemical Sciences (2)
- Climate Change (1)
- Computer Science (10)
- Coronavirus (1)
- Critical Materials (2)
- Cybersecurity (1)
- Energy Storage (9)
- Environment (3)
- Exascale Computing (1)
- Frontier (1)
- Fusion (4)
- Isotopes (1)
- Machine Learning (3)
- Materials (1)
- Materials Science (31)
- Mathematics (1)
- Microscopy (6)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (12)
- National Security (1)
- Neutron Science (10)
- Nuclear Energy (6)
- Physics (8)
- Polymers (4)
- Quantum Science (4)
- Security (1)
- Summit (3)
- Sustainable Energy (6)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (2)
- Transportation (3)
Media Contacts
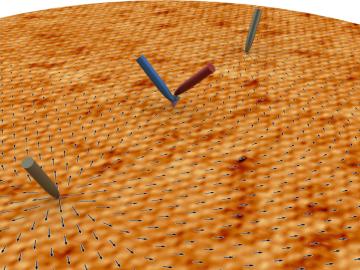
Liam Collins was drawn to study physics to understand “hidden things” and honed his expertise in microscopy so that he could bring them to light.
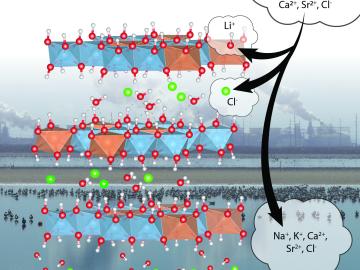
In the quest for domestic sources of lithium to meet growing demand for battery production, scientists at ORNL are advancing a sorbent that can be used to more efficiently recover the material from brine wastes at geothermal power plants.
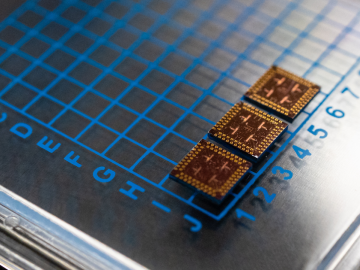
Scientists at have experimentally demonstrated a novel cryogenic, or low temperature, memory cell circuit design based on coupled arrays of Josephson junctions, a technology that may be faster and more energy efficient than existing memory devices.

Eugene P. Wigner Fellow Victor Fung’s story is proof that a series of positive experiences around science and happy accidents can lead to a rewarding research career. He joined ORNL in 2019.
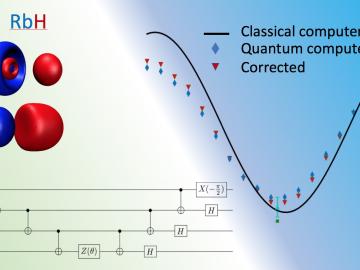
Researchers at ORNL have developed a quantum chemistry simulation benchmark to evaluate the performance of quantum devices and guide the development of applications for future quantum computers.


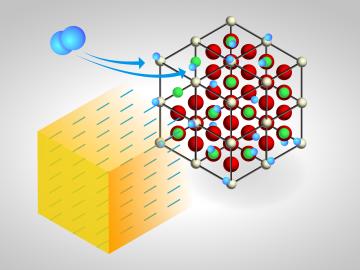
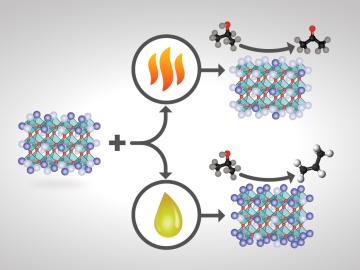
For some crystalline catalysts, what you see on the surface is not always what you get in the bulk, according to two studies led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The investigators discovered that treating a complex