
Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (1)
- (-) Frontier (15)
- (-) Fusion (3)
- (-) Grid (3)
- (-) Isotopes (8)
- (-) Nanotechnology (10)
- (-) Neutron Science (11)
- (-) Physics (15)
- (-) Summit (8)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (6)
- Artificial Intelligence (15)
- Big Data (3)
- Bioenergy (4)
- Biology (4)
- Biomedical (6)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (3)
- Chemical Sciences (16)
- Composites (4)
- Computer Science (17)
- Coronavirus (2)
- Critical Materials (5)
- Cybersecurity (1)
- Energy Storage (6)
- Environment (8)
- Exascale Computing (12)
- High-Performance Computing (18)
- Irradiation (1)
- Machine Learning (4)
- Materials (42)
- Materials Science (14)
- Microscopy (8)
- Molten Salt (1)
- National Security (3)
- Nuclear Energy (7)
- Partnerships (6)
- Polymers (8)
- Quantum Computing (8)
- Quantum Science (6)
- Security (1)
- Simulation (9)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (1)
- Transportation (5)
Media Contacts

A new nanoscience study led by a researcher at ORNL takes a big-picture look at how scientists study materials at the smallest scales.
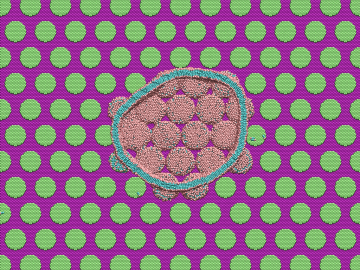
Timothy Gray of ORNL led a study that may have revealed an unexpected change in the shape of an atomic nucleus. The surprise finding could affect our understanding of what holds nuclei together, how protons and neutrons interact and how elements form.

Wildfires have shaped the environment for millennia, but they are increasing in frequency, range and intensity in response to a hotter climate. The phenomenon is being incorporated into high-resolution simulations of the Earth’s climate by scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, with a mission to better understand and predict environmental change.
Over the past decade, teams of engineers, chemists and biologists have analyzed the physical and chemical properties of cicada wings, hoping to unlock the secret of their ability to kill microbes on contact. If this function of nature can be replicated by science, it may lead to products with inherently antibacterial surfaces that are more effective than current chemical treatments.
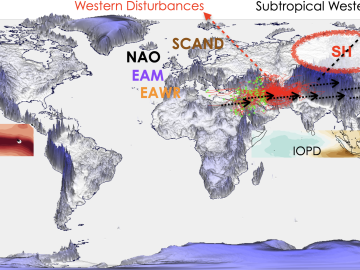
As extreme weather devastates communities worldwide, scientists are using modeling and simulation to understand how climate change impacts the frequency and intensity of these events. Although long-term climate projections and models are important, they are less helpful for short-term prediction of extreme weather that may rapidly displace thousands of people or require emergency aid.

With the world’s first exascale supercomputer now fully open for scientific business, researchers can thank the early users who helped get the machine up to speed.

Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory were the first to use neutron reflectometry to peer inside a working solid-state battery and monitor its electrochemistry.

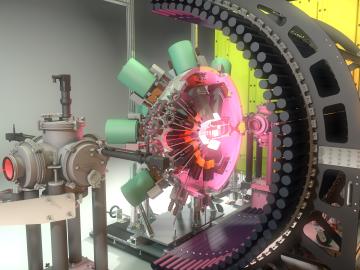
Creating energy the way the sun and stars do — through nuclear fusion — is one of the grand challenges facing science and technology. What’s easy for the sun and its billions of relatives turns out to be particularly difficult on Earth.
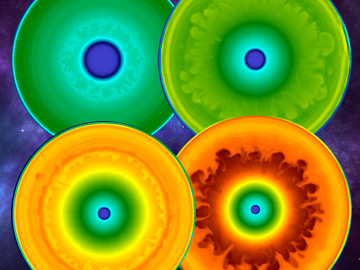
As a result of largescale 3D supernova simulations conducted on the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility’s Summit supercomputer by researchers from the University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, astrophysicists now have the most complete picture yet of what gravitational waves from exploding stars look like.

An advance in a topological insulator material — whose interior behaves like an electrical insulator but whose surface behaves like a conductor — could revolutionize the fields of next-generation electronics and quantum computing, according to scientists at ORNL.


