
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (5)
- Computer Science (1)
- Energy Science (28)
- Fusion and Fission (3)
- Fusion Energy (9)
- Materials (31)
- Materials for Computing (1)
- National Security (4)
- Neutron Science (10)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (13)
- Quantum information Science (4)
- Supercomputing (14)
News Topics
- (-) Bioenergy (22)
- (-) Composites (3)
- (-) Cybersecurity (9)
- (-) Fusion (18)
- (-) Microscopy (13)
- (-) Nanotechnology (23)
- (-) Space Exploration (6)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (43)
- Advanced Reactors (21)
- Artificial Intelligence (20)
- Big Data (18)
- Biology (5)
- Biomedical (27)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (1)
- Chemical Sciences (5)
- Clean Water (7)
- Computer Science (74)
- Coronavirus (25)
- Critical Materials (2)
- Energy Storage (29)
- Environment (48)
- Exascale Computing (5)
- Frontier (3)
- Grid (12)
- High-Performance Computing (3)
- Isotopes (9)
- Machine Learning (13)
- Materials (2)
- Materials Science (57)
- Mathematics (2)
- Mercury (2)
- Molten Salt (3)
- National Security (2)
- Neutron Science (56)
- Nuclear Energy (48)
- Physics (19)
- Polymers (9)
- Quantum Science (24)
- Security (5)
- Summit (26)
- Transportation (27)
Media Contacts

Matthew R. Ryder, a researcher at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been named the 2020 Foresight Fellow in Molecular-Scale Engineering.

Temperatures hotter than the center of the sun. Magnetic fields hundreds of thousands of times stronger than the earth’s. Neutrons energetic enough to change the structure of a material entirely.

ITER, the world’s largest international scientific collaboration, is beginning assembly of the fusion reactor tokamak that will include 12 different essential hardware systems provided by US ITER, which is managed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

As a teenager, Kat Royston had a lot of questions. Then an advanced-placement class in physics convinced her all the answers were out there.
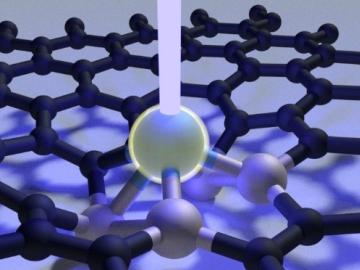
Scientists at Oak Ridge National Laboratory used a focused beam of electrons to stitch platinum-silicon molecules into graphene, marking the first deliberate insertion of artificial molecules into a graphene host matrix.

The techniques Theodore Biewer and his colleagues are using to measure whether plasma has the right conditions to create fusion have been around awhile.

Biological membranes, such as the “walls” of most types of living cells, primarily consist of a double layer of lipids, or “lipid bilayer,” that forms the structure, and a variety of embedded and attached proteins with highly specialized functions, including proteins that rapidly and selectively transport ions and molecules in and out of the cell.

Scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a new method to peer deep into the nanostructure of biomaterials without damaging the sample. This novel technique can confirm structural features in starch, a carbohydrate important in biofuel production.

The prospect of simulating a fusion plasma is a step closer to reality thanks to a new computational tool developed by scientists in fusion physics, computer science and mathematics at ORNL.

Rigoberto “Gobet” Advincula has been named Governor’s Chair of Advanced and Nanostructured Materials at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the University of Tennessee.


