
Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (14)
- (-) Bioenergy (19)
- (-) Machine Learning (10)
- (-) Nanotechnology (9)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (12)
- Advanced Reactors (4)
- Big Data (9)
- Biology (28)
- Biomedical (6)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (16)
- Chemical Sciences (15)
- Clean Water (5)
- Climate Change (26)
- Composites (3)
- Computer Science (20)
- Coronavirus (9)
- Critical Materials (4)
- Cybersecurity (7)
- Decarbonization (21)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (25)
- Environment (36)
- Exascale Computing (8)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (10)
- Fusion (7)
- Grid (13)
- High-Performance Computing (16)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (1)
- Isotopes (4)
- ITER (2)
- Materials (37)
- Materials Science (16)
- Mercury (1)
- Microscopy (13)
- National Security (17)
- Net Zero (2)
- Neutron Science (12)
- Nuclear Energy (10)
- Partnerships (8)
- Physics (10)
- Polymers (5)
- Quantum Computing (7)
- Quantum Science (9)
- Security (4)
- Simulation (6)
- Space Exploration (4)
- Summit (7)
- Sustainable Energy (25)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (2)
- Transportation (10)
Media Contacts

The rapid pace of global climate change has added urgency to developing technologies that reduce the carbon footprint of transportation technologies, especially in sectors that are difficult to electrify.

A force within the supercomputing community, Jack Dongarra developed software packages that became standard in the industry, allowing high-performance computers to become increasingly more powerful in recent decades.

The Center for Bioenergy Innovation at ORNL offers a unique opportunity for early career scientists to conduct groundbreaking research while learning what it takes to manage a large collaborative science center.
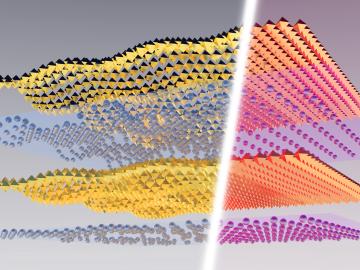
A study by researchers at the ORNL takes a fresh look at what could become the first step toward a new generation of solar batteries.

Bryan Piatkowski, a Liane Russell Distinguished Fellow in the Biosciences Division at ORNL, is exploring the genetic pathways for traits such as stress tolerance in several plant species important for carbon sequestration
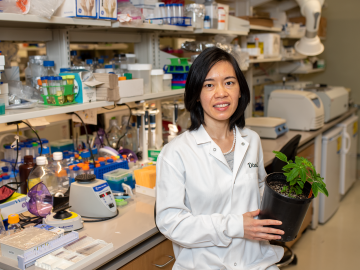
A team of researchers working within the Center for Bioenergy Innovation at ORNL has discovered a pathway to encourage a type of lignin formation in plants that could make the processing of crops grown for products such as sustainable jet fuels easier and less costly.

ORNL, TVA and TNECD were recognized by the Federal Laboratory Consortium for their impactful partnership that resulted in a record $2.3 billion investment by Ultium Cells, a General Motors and LG Energy Solution joint venture, to build a battery cell manufacturing plant in Spring Hill, Tennessee.
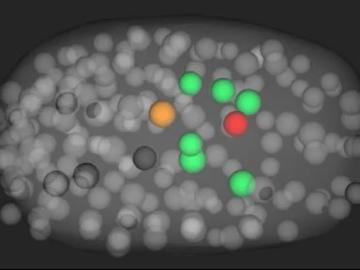
Scientists have developed a novel approach to computationally infer previously undetected behaviors within complex biological environments by analyzing live, time-lapsed images that show the positioning of embryonic cells in C. elegans, or roundworms. Their published methods could be used to reveal hidden biological activity.
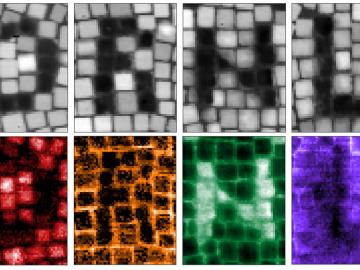
Drilling with the beam of an electron microscope, scientists at ORNL precisely machined tiny electrically conductive cubes that can interact with light and organized them in patterned structures that confine and relay light’s electromagnetic signal.
A team of scientists led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the Georgia Institute of Technology is using supercomputing and revolutionary deep learning tools to predict the structures and roles of thousands of proteins with unknown functions.


