Filter News
Area of Research
News Topics
- (-) Net Zero (2)
- (-) Quantum Science (9)
- (-) Summit (7)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (12)
- Advanced Reactors (4)
- Artificial Intelligence (14)
- Big Data (9)
- Bioenergy (19)
- Biology (28)
- Biomedical (6)
- Biotechnology (3)
- Buildings (16)
- Chemical Sciences (15)
- Clean Water (5)
- Climate Change (26)
- Composites (3)
- Computer Science (20)
- Coronavirus (9)
- Critical Materials (4)
- Cybersecurity (7)
- Decarbonization (21)
- Element Discovery (1)
- Energy Storage (25)
- Environment (36)
- Exascale Computing (8)
- Fossil Energy (1)
- Frontier (10)
- Fusion (7)
- Grid (13)
- High-Performance Computing (16)
- Hydropower (8)
- Irradiation (1)
- Isotopes (4)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (10)
- Materials (37)
- Materials Science (16)
- Mercury (1)
- Microscopy (13)
- Nanotechnology (9)
- National Security (17)
- Neutron Science (12)
- Nuclear Energy (10)
- Partnerships (8)
- Physics (10)
- Polymers (5)
- Quantum Computing (7)
- Security (4)
- Simulation (6)
- Space Exploration (4)
- Sustainable Energy (25)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (2)
- Transportation (10)
Media Contacts
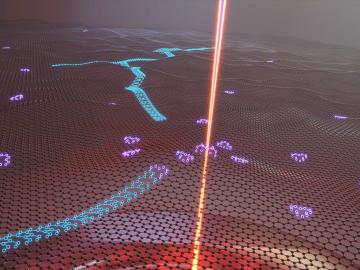
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers serendipitously discovered when they automated the beam of an electron microscope to precisely drill holes in the atomically thin lattice of graphene, the drilled holes closed up.

Matthew Craig grew up eagerly exploring the forest patches and knee-high waterfalls just beyond his backyard in central Illinois’ corn belt. Today, that natural curiosity and the expertise he’s cultivated in biogeochemistry and ecology are focused on how carbon cycles in and out of soils, a process that can have tremendous impact on the Earth’s climate.

U.S. Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm visited Oak Ridge National Laboratory today to attend a groundbreaking ceremony for the U.S. Stable Isotope Production and Research Center. The facility is slated to receive $75 million in funding from the Inflation Reduction Act.
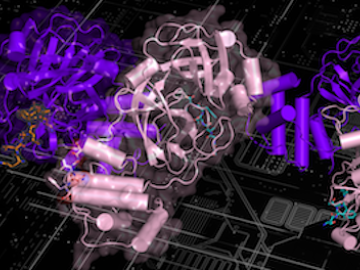
A new paper published in Nature Communications adds further evidence to the bradykinin storm theory of COVID-19’s viral pathogenesis — a theory that was posited two years ago by a team of researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory.

Five National Quantum Information Science Research Centers are leveraging the behavior of nature at the smallest scales to develop technologies for science’s most complex problems.

Travis Humble has been named director of the Quantum Science Center headquartered at ORNL. The QSC is a multi-institutional partnership that spans industry, academia and government institutions and is tasked with uncovering the full potential of quantum materials, sensors and algorithms.

Scientists at ORNL used neutron scattering to determine whether a specific material’s atomic structure could host a novel state of matter called a spiral spin liquid.

What’s getting Jim Szybist fired up these days? It’s the opportunity to apply his years of alternative fuel combustion and thermodynamics research to the challenge of cleaning up the hard-to-decarbonize, heavy-duty mobility sector — from airplanes to locomotives to ships and massive farm combines.

ORNL researchers used the nation’s fastest supercomputer to map the molecular vibrations of an important but little-studied uranium compound produced during the nuclear fuel cycle for results that could lead to a cleaner, safer world.

A force within the supercomputing community, Jack Dongarra developed software packages that became standard in the industry, allowing high-performance computers to become increasingly more powerful in recent decades.




