
Filter News
Area of Research
- (-) Supercomputing (60)
- Advanced Manufacturing (1)
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (87)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Clean Energy (47)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (2)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (1)
- Computer Science (1)
- Fusion and Fission (9)
- Fusion Energy (1)
- Isotope Development and Production (1)
- Isotopes (8)
- Materials (26)
- Materials for Computing (2)
- National Security (19)
- Neutron Science (19)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (10)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Biomedical (12)
- (-) Environment (16)
- (-) Frontier (25)
- (-) Machine Learning (12)
- (-) Mathematics (1)
- (-) Space Exploration (2)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (5)
- Artificial Intelligence (33)
- Big Data (14)
- Bioenergy (9)
- Biology (10)
- Biotechnology (2)
- Buildings (3)
- Chemical Sciences (4)
- Climate Change (15)
- Computer Science (76)
- Coronavirus (12)
- Cybersecurity (8)
- Decarbonization (4)
- Energy Storage (6)
- Exascale Computing (19)
- Grid (4)
- High-Performance Computing (31)
- Isotopes (1)
- Materials (12)
- Materials Science (14)
- Microscopy (7)
- Molten Salt (1)
- Nanotechnology (10)
- National Security (8)
- Net Zero (1)
- Neutron Science (13)
- Nuclear Energy (3)
- Partnerships (1)
- Physics (7)
- Quantum Computing (15)
- Quantum Science (20)
- Security (5)
- Simulation (11)
- Software (1)
- Summit (35)
- Sustainable Energy (8)
- Transportation (5)
Media Contacts

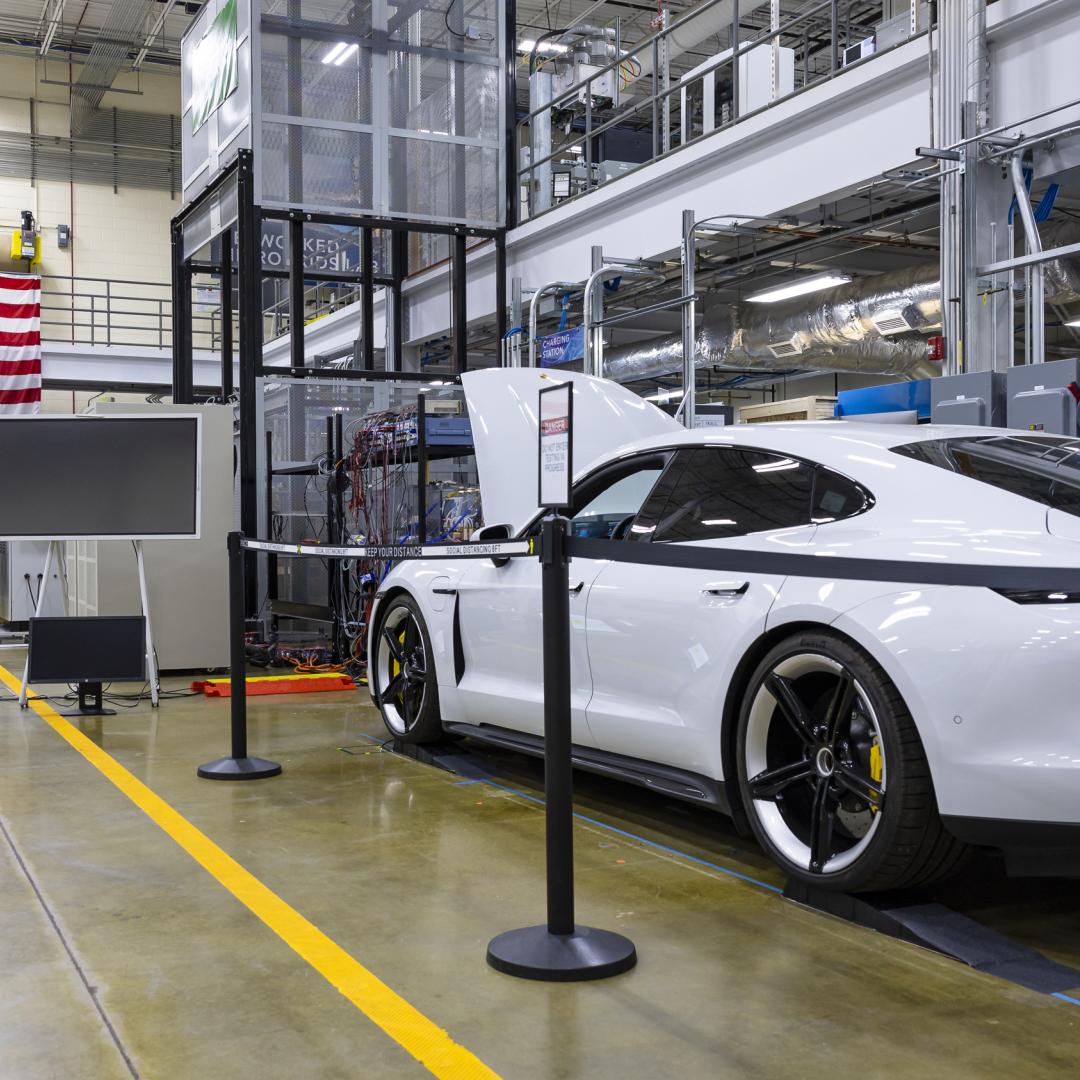
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment, or INCITE, program is seeking proposals for high-impact, computationally intensive research campaigns in a broad array of science, engineering and computer science domains.
Twenty-seven ORNL researchers Zoomed into 11 middle schools across Tennessee during the annual Engineers Week in February. East Tennessee schools throughout Oak Ridge and Roane, Sevier, Blount and Loudon counties participated, with three West Tennessee schools joining in.

The U.S. Air Force and Oak Ridge National Laboratory launched a new high-performance weather forecasting computer system that will provide a platform for some of the most advanced weather modeling in the world.

Six scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory were named Battelle Distinguished Inventors, in recognition of obtaining 14 or more patents during their careers at the lab.

A multi-institutional team, led by a group of investigators at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been studying various SARS-CoV-2 protein targets, including the virus’s main protease. The feat has earned the team a finalist nomination for the Association of Computing Machinery, or ACM, Gordon Bell Special Prize for High Performance Computing-Based COVID-19 Research.
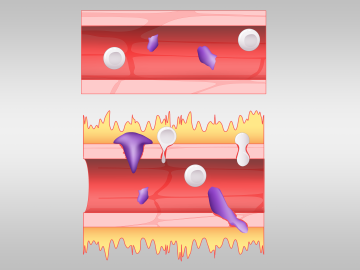
A team led by Dan Jacobson of Oak Ridge National Laboratory used the Summit supercomputer at ORNL to analyze genes from cells in the lung fluid of nine COVID-19 patients compared with 40 control patients.
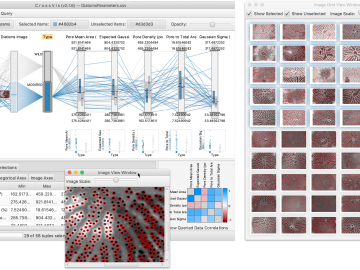
From materials science and earth system modeling to quantum information science and cybersecurity, experts in many fields run simulations and conduct experiments to collect the abundance of data necessary for scientific progress.
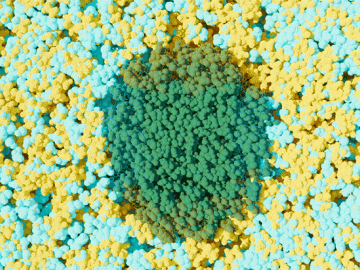
Scientists at ORNL used neutron scattering and supercomputing to better understand how an organic solvent and water work together to break down plant biomass, creating a pathway to significantly improve the production of renewable

Scientists from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and a dozen other international research institutions have produced the most elaborate set of projections to date that illustrates possible futures for major monsoon regions.
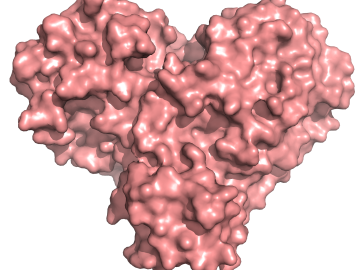
A team of researchers has performed the first room-temperature X-ray measurements on the SARS-CoV-2 main protease — the enzyme that enables the virus to reproduce.


