Filter News
Area of Research
- Biological Systems (1)
- Biology and Environment (68)
- Biology and Soft Matter (1)
- Clean Energy (40)
- Climate and Environmental Systems (1)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Fusion and Fission (5)
- Isotopes (4)
- Materials (19)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- National Security (6)
- Neutron Science (10)
- Quantum information Science (1)
- Supercomputing (36)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Biomedical (32)
- (-) Buildings (28)
- (-) Clean Water (16)
- (-) Environment (111)
- (-) Exascale Computing (29)
- (-) Fossil Energy (4)
- (-) Mercury (7)
- (-) Nanotechnology (20)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (47)
- Advanced Reactors (9)
- Artificial Intelligence (52)
- Big Data (32)
- Bioenergy (52)
- Biology (61)
- Biotechnology (13)
- Chemical Sciences (29)
- Climate Change (56)
- Composites (9)
- Computer Science (94)
- Coronavirus (18)
- Critical Materials (6)
- Cybersecurity (14)
- Decarbonization (51)
- Education (1)
- Emergency (2)
- Energy Storage (36)
- Frontier (27)
- Fusion (33)
- Grid (28)
- High-Performance Computing (48)
- Hydropower (5)
- Isotopes (32)
- ITER (2)
- Machine Learning (24)
- Materials (45)
- Materials Science (56)
- Mathematics (7)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (23)
- Molten Salt (1)
- National Security (49)
- Net Zero (8)
- Neutron Science (54)
- Nuclear Energy (61)
- Partnerships (21)
- Physics (36)
- Polymers (11)
- Quantum Computing (22)
- Quantum Science (33)
- Renewable Energy (1)
- Security (13)
- Simulation (33)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (12)
- Statistics (1)
- Summit (31)
- Sustainable Energy (51)
- Transformational Challenge Reactor (3)
- Transportation (32)
Media Contacts

Katy Bradford is on a mission to revolutionize the construction industry and is the founder of Cassette Construction, a company in the newest cohort of Innovation Crossroads, a DOE Lab-Embedded Entrepreneurship Program node at ORNL. As an Innovation Crossroads fellow, Bradford and her company will receive technical, financial and networking support to successfully advance the company’s products to the marketplace.
After retiring from Y-12, Scott Abston joined the Isotope Science and Engineering Directorate to support isotope production and work with his former manager. He now leads a team maintaining critical equipment for medical and space applications. Abston finds fulfillment in mentoring his team and is pleased with his decision to continue working.

Office of Science to announce a new research and development opportunity led by ORNL to advance technologies and drive new capabilities for future supercomputers. This industry research program worth $23 million, called New Frontiers, will initiate partnerships with multiple companies to accelerate the R&D of critical technologies with renewed emphasis on energy efficiency for the next generation of post-exascale computing in the 2029 and beyond time frame.

As a mechanical engineer in building envelope materials research at ORNL, Bryan Maldonado sees opportunities to apply his scientific expertise virtually everywhere he goes, from coast to coast. As an expert in understanding how complex systems operate, he’s using machine learning methods to control the process and ultimately optimize performance.

Nuclear physicists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently used Frontier, the world’s most powerful supercomputer, to calculate the magnetic properties of calcium-48’s atomic nucleus.

ORNL’s Joshua New was named the 2024 Researcher of the Year by R&D World magazine as part of its R&D 100 Professional Award winners.

Jeremiah Sewell leads a team at ORNL, working on xenon-129 production for lung imaging. Reflecting on his career, Sewell views each opportunity as a "door" he steps through, leveraging over 25 years of experience in nuclear power and centrifuge operations to advance the facility’s mission.
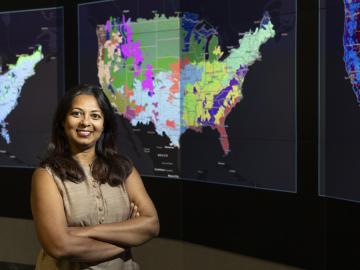
Debjani Singh, a senior scientist at ORNL, leads the HydroSource project, which enhances hydropower research by making water data more accessible and useful. With a background in water resources, data science, and earth science, Singh applies innovative tools like AI to advance research. Her career, shaped by her early exposure to science in India, focuses on bridging research with practical applications.

A study found that beaches with manmade fortifications recover more slowly from hurricanes than natural beaches, losing more sand and vegetation. The researchers used satellite images and light detection and ranging data, or LIDAR, to measure elevation changes and vegetation coverage. Changes in elevation showed how much sand was depleted during the storm and how much sand returned throughout the following year.

Five researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory recently completed an eight-week pilot commercialization coaching program as part of Safari, a program funded by DOE’s Office of Technology Transitions, or OTT, Practices to Accelerate the Commercialization of Technologies, or PACT.


