
Filter News
Area of Research
- Advanced Manufacturing (3)
- Biology and Environment (18)
- Computational Biology (1)
- Computational Engineering (2)
- Computer Science (4)
- Energy Science (17)
- Fusion and Fission (18)
- Fusion Energy (13)
- Materials (24)
- Materials for Computing (3)
- Mathematics (1)
- National Security (10)
- Neutron Science (80)
- Nuclear Science and Technology (17)
- Nuclear Systems Modeling, Simulation and Validation (1)
- Supercomputing (31)
News Type
News Topics
- (-) Advanced Reactors (25)
- (-) Artificial Intelligence (92)
- (-) Clean Water (30)
- (-) Fusion (47)
- (-) Neutron Science (109)
- (-) Security (17)
- 3-D Printing/Advanced Manufacturing (89)
- Big Data (62)
- Bioenergy (84)
- Biology (100)
- Biomedical (53)
- Biotechnology (28)
- Buildings (50)
- Chemical Sciences (48)
- Composites (21)
- Computer Science (153)
- Coronavirus (30)
- Critical Materials (17)
- Cybersecurity (17)
- Education (2)
- Emergency (4)
- Energy Storage (64)
- Environment (164)
- Exascale Computing (52)
- Fossil Energy (7)
- Frontier (45)
- Grid (54)
- High-Performance Computing (93)
- Hydropower (12)
- Irradiation (2)
- Isotopes (38)
- ITER (7)
- Machine Learning (51)
- Materials (87)
- Materials Science (89)
- Mathematics (11)
- Mercury (10)
- Microelectronics (3)
- Microscopy (34)
- Molten Salt (7)
- Nanotechnology (29)
- National Security (63)
- Nuclear Energy (85)
- Partnerships (37)
- Physics (38)
- Polymers (18)
- Quantum Computing (39)
- Quantum Science (58)
- Simulation (51)
- Software (1)
- Space Exploration (23)
- Statistics (3)
- Summit (48)
- Transportation (66)
Media Contacts

Kathryn McCarthy, director of the US ITER Project at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, has been awarded the 2024 E. Gail de Planque Medal by the American Nuclear Society.

Researchers used the Summit supercomputer at ORNL to answer one of fission’s big questions: What exactly happens during the nucleus’s “neck rupture” as it splits in two? Scission neutrons have been theorized to be among those particles emitted during neck rupture, although their exact characteristics have been debated due to a lack of conclusive experimental evidence of their existence.

Biochemist David Baker — just announced as a recipient of the Nobel Prize for Chemistry — turned to the High Flux Isotope Reactor (HFIR) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory for information he couldn’t get anywhere else. HFIR is the strongest reactor-based neutron source in the United States.

To bridge the gap between experimental facilities and supercomputers, experts from SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory are teaming up with other DOE national laboratories to build a new data streaming pipeline. The pipeline will allow researchers to send their data to the nation’s leading computing centers for analysis in real time even as their experiments are taking place.

Prasanna Balprakash, director of AI programs for ORNL, discussed advancing climate and weather research through high performance computing and artificial intelligence as part of a September 18 panel for the United States Senate.

The Smoky Mountain Computational Sciences and Engineering Conference, or SMC24, entered its third decade with the 21st annual gathering in East Tennessee.

Scientists at ORNL used neutrons to end a decades-long debate about an enzyme cancer uses.

ORNL's Spallation Neutron Source, the nation’s leading source of pulsed neutron beams for research, was recently restarted after nine months of upgrade work.

Distinguished materials scientist Takeshi Egami has spent his career revealing the complex atomic structure of metallic glass and other liquids — sometimes sharing theories with initially resistant minds in the scientific community.
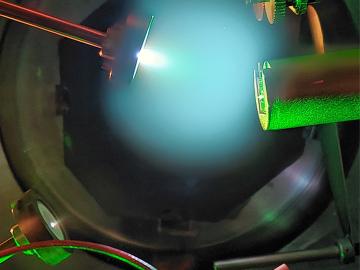
In a game-changing study, ORNL scientists developed a deep learning model — a type of artificial intelligence that mimics human brain function — to analyze high-speed videos of plasma plumes during a process called pulsed laser deposition.


